Batteries overheat and lose capacity over time, so rigorous testing is essential. Battery load testing measures the battery’s voltage, current, and power under various load conditions, thereby assessing the battery’s performance, safety, and stability. For custom lithium-ion batteries, this test predicts battery life, optimizes cost-effectiveness, and ensures batteries meet industry standards. This article dives into the importance, types, procedures, and results of battery load tests.
Key Takeaways:
- Rigorous battery load testing evaluates battery degradation and capacity, helping to extend battery life and enhance manufacturers’ regulatory compliance and market competitiveness.
- Reliable load test procedure. Check the battery’s state of charge and connect it with the tester. Then test the battery under load and interpret the load results.
- Optimizing charging strategies, cell structure, topology design, and calibrating the battery management system are effective methods to optimize load testing results.
What is battery load testing?
Battery load testing evaluates battery performance and health status under simulated load. This procedure measures key parameters, like capacity, voltage, and internal resistance, to assess the battery’s ability to deliver power and state of health. For lithium-ion batteries, battery load testing helps understand battery performance and life, which is of great significance for battery selection and maintenance.

Why Battery Load Testing Matters?
Battery load test is not only vital to ensure superior safety, extended battery lifespan, but also critical for engineers to optimize cost-effectiveness and boost market competitiveness.
- Overall evaluation of battery performance. Test the battery’s overall capacity, efficiency, and cycle life by simulating over-current, short circuit, high, and low temperature conditions. This helps users analyze battery quality in an efficient way.
- Optimize supply chain and cost control. Regular testing monitors battery health, optimizes charge strategies, extends service life, and reduces costs due to frequent battery replacements. The test data is a key indicator for selecting a reliable battery manufacturer.
- Improve compliance and market competitiveness. Many international safety standards require lithium-ion batteries to pass battery load tests, such as UN38.3, IEC62133, and UL2054. Enterprises ensure batteries comply with transportation and usage regulations, which builds customer confidence.
- Enhance security risk management and mitigation. Battery load testing identifies risks such as overload, short circuit, and aging to avoid device downtime and data loss. It provides security assurance for enterprises and reduces the probability of corporate liability disputes.
The Principle of Battery Load Testing
Understanding the basic principle of battery load testing is pivotal in conducting actual operating procedures.
- Battery load test simulates the battery’s actual operating conditions by applying a load to the battery to assess its capacity and performance.
- The battery generates current under load. This current flows through the load resistor, producing a voltage drop proportional to the current.
- Next, determine battery capacity, internal resistance, and discharge curve by monitoring changes in battery voltage and current, thereby assessing battery performance.
What are the types of battery load testing?
Different types of load tests stimulate actual conditions, identifying battery bulges, leaks, or thermal runaway. Thus, understanding some common types of battery load testing is critical.
| Types | Principle | Function |
| Constant current load test | Applies stable constant current loads on batteries and measures voltage changes under varying loads. | Assess battery capacity and health status |
| Pulse Load Test | Applies periodic load pulses to the battery, stimulates high-power demands and observes the output voltage fluctuations. | Evaluate the battery’s transient load response, recovery capability, and BMS protection. |
| Capacity Load Test | Discharge battery at constant current until reaching the defined voltage and capacity through constant current discharge. | Verify the battery’s true capacity, performance stability, and lifespan prediction. |
| Cycle Life Load Test | Perform charge and discharge cycles to observe the battery’s capacity retention and internal resistance changes | Evaluate the battery’s service life, reliability, and uniformity evaluation |
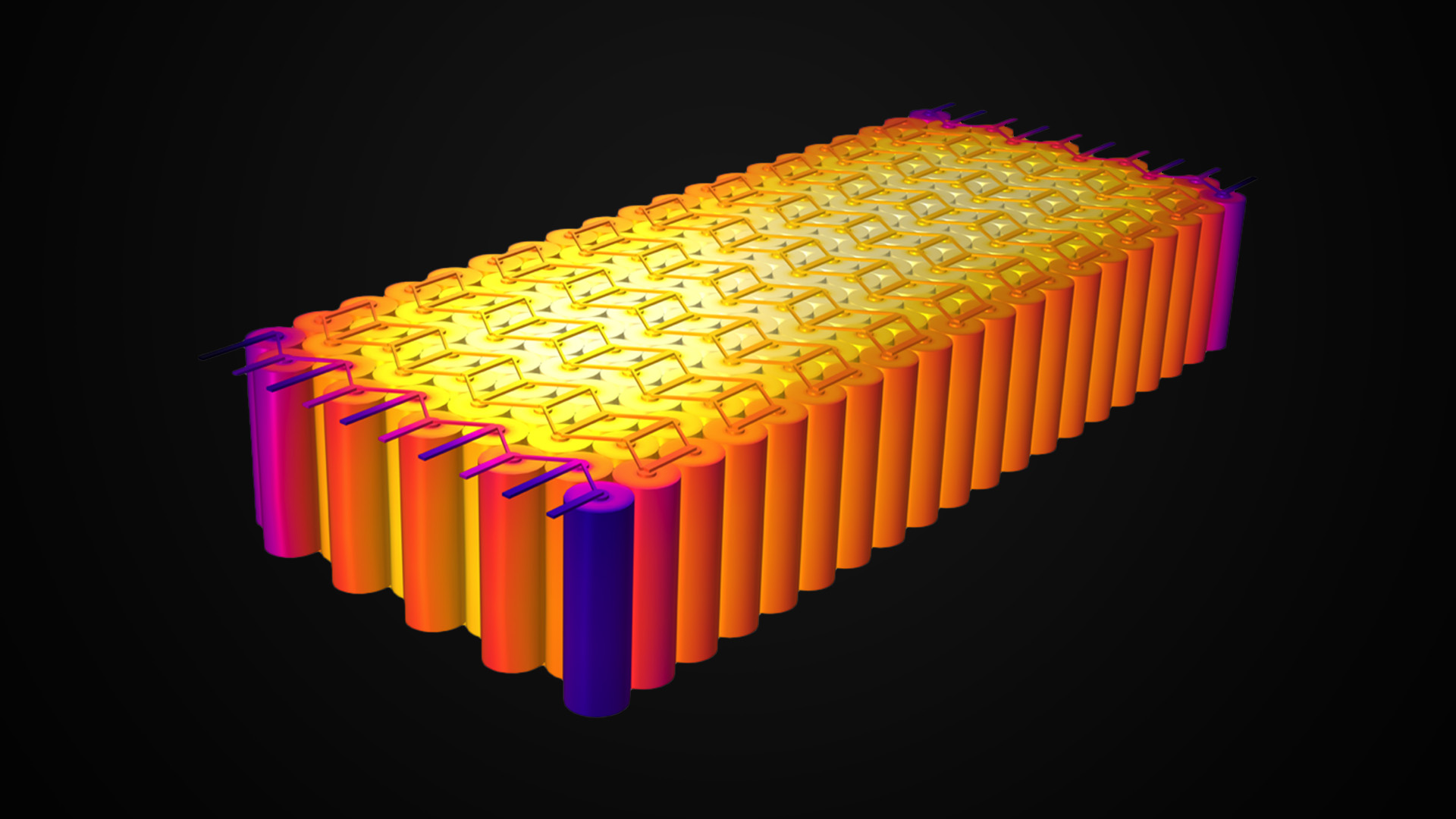
| High/Low Temperature Performance Load Test | Assess the battery supply’s load capacity and heat dissipation performance by monitoring the temperature changes during load operation. | Identify potential problems in high or low temperature conditions and improve the battery’s reliability and stability. |
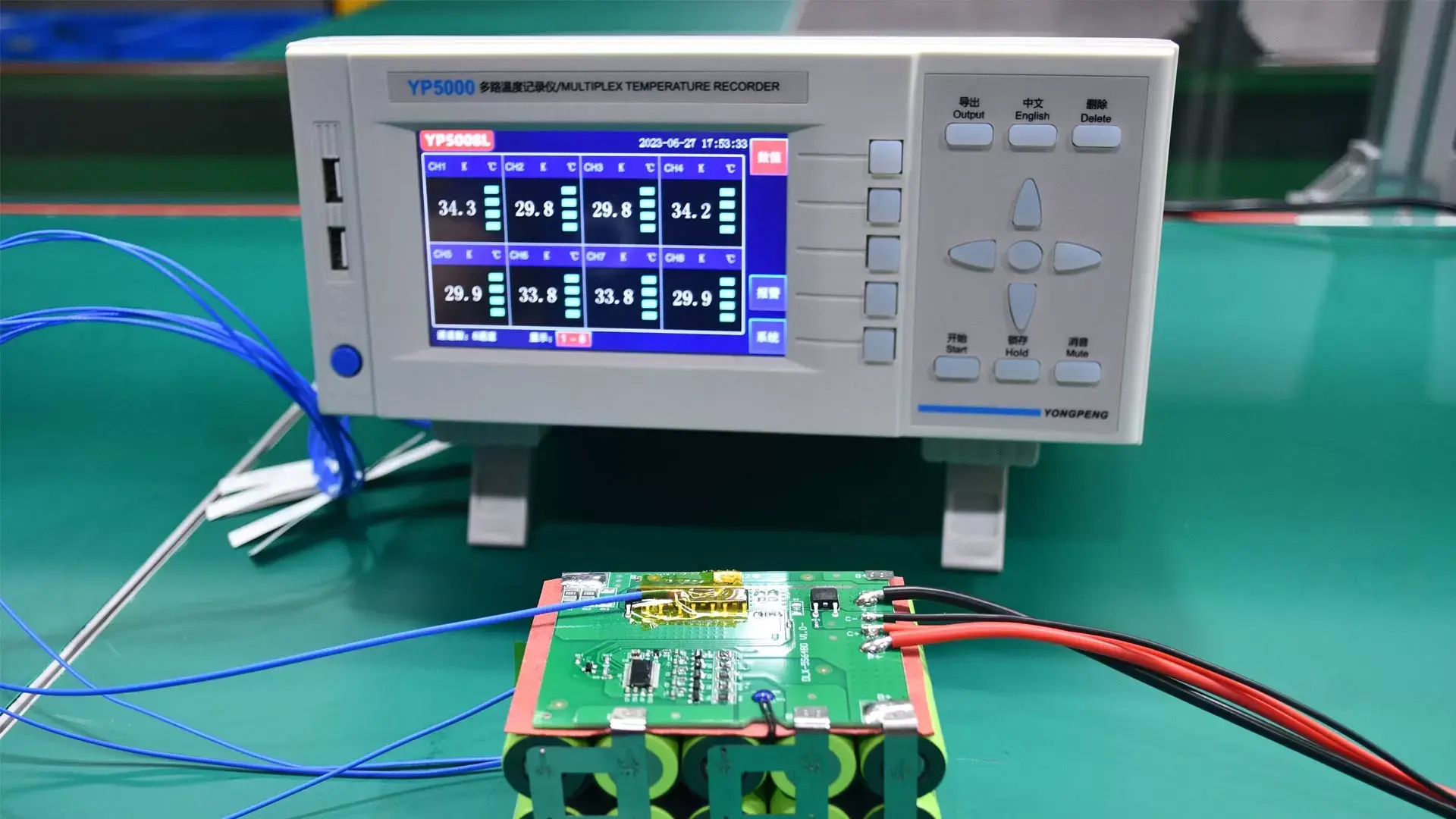
Battery Load Testing Equipment
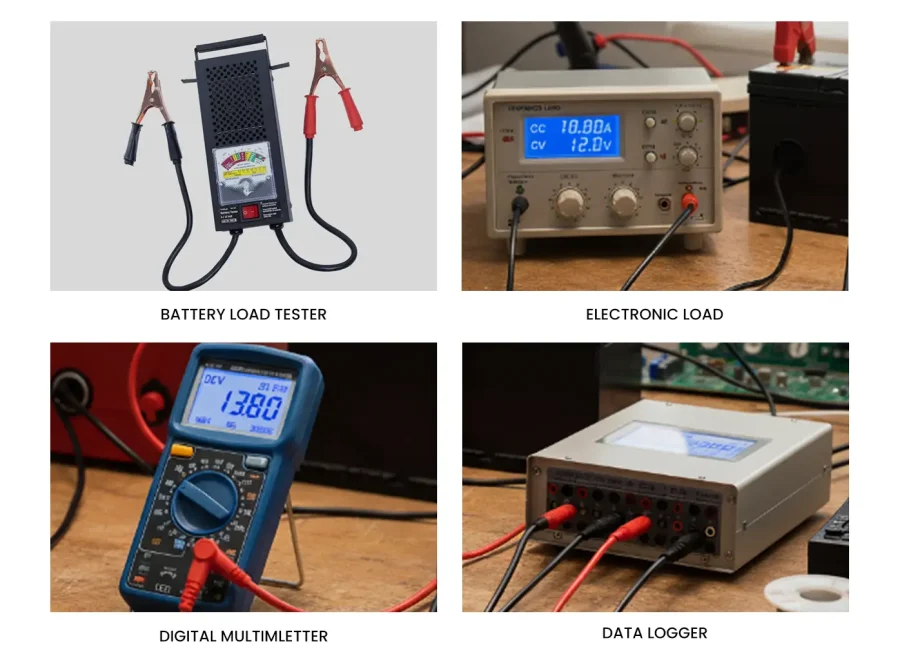
Before performing battery load testing, understanding and checking the battery load test equipment is an essential step.
- Electronic Load. It is an electronic device that accurately controls the load current, power, or resistance value. It features high precision, powerful functions, a built-in data recording function, and direct draw discharge curves.
- Battery Load Tester. It is an integrated portable device that contains a load module, voltmeter, ammeter, and built-in algorithms. This is a professional tool for starting battery maintenance.
- Digital Multimeter. Measure the battery’s open-circuit voltage and loaded voltage. High-quality multimeters capture the voltage drop when applying a load. It is best to have a data or minimum value recording function to capture the lowest voltage under load.
- Data Logger. It records voltage, current, and temperature changes throughout the test process for further analysis of discharge curves and performance trends. Many advanced electronic loads and testers have this function.

How to Perform a Battery Load Test?
Conducting a battery load test on lithium-ion batteries includes the following steps:
Step1. Safety First and Check State of Charge
- Wear safety goggles, and ensure the work area is well ventilated before the test. Then, inspect the battery’s state for bulging, leakage, deformation, or unusual odor. Next, check the battery’s terminals and make sure they are clean.
- Use a multimeter to check the battery’s state of charge. For lithium-ion batteries, they require retaining a state of charge above 80% before the load test, which is vital for the accuracy of the test.
Step2. Connect the Load Tester with the Battery
Choose a compatible load tester for lithium-ion battery packs, ensuring it measures the voltage and current range.
- Connect devices. Connect the red (+) clip of the tester to the positive terminal of the battery. Attach the black (-) clip to its negative terminal.
- Ensure the stability and security of the connection to avoid damage or interruption.
Step3. Apply the Load and Keep Monitoring
- Parameter Settings. Confirm the battery’s voltage level, capacity, or CCA value when set load status is set. For the capacity test, set the discharge current and cutoff voltage.
- Start the load tester. Once you connect the load tester, apply a load to the batteries. Closely monitor the voltage drop and battery temperature. Use a multimeter to monitor the battery voltage in real time to verify if the readings of the load tester are accurate.
Step4. Record Test Results and Judge Performance
- Stop the load test immediately when it reaches the cut-off voltage. Record the readings of capacity, voltage, and abnormal situations, and then compare the results with the information provided by the supplier to assess the battery’s performance.
- Focus on the signs that indicate battery degradation. Prioritize battery maintenance and replacement when there are signs of rapid voltage drops, increased internal resistance, abnormal temperature rise, or capacity decay.

Interpret Battery Load Test Results
Understanding battery load testing results is conducive to assessing battery performance and adopting optimization solutions. The battery’s voltage, current, temperature, internal resistance, and capacity are major points to explain these results.
- Voltage. Monitor battery voltage using a load tester or a multimeter. Healthy batteries maintain stable voltage output during the load test. In contrast, rapid voltage drops indicate the battery’s degraded capacity and internal fault. Significant voltage fluctuations reflect the uneven chemical reaction inside the battery.
- Capacity. Assess the battery’s capacity retention ability under the capacity load test. If the actual capacity is lower than the rated capacity, it indicates that the battery is aging, damaged, or has internal losses.
- Current. Lower current indicates increased internal resistance or a load fault. Excessive current indicates a short circuit in the load or an abnormal battery output voltage.
- Power. Record the battery’s maximum power. It reflects the battery’s output capability under specific load conditions and is vital for devices needing high power output, such as power tools, robots.
- Internal Resistance. The pulse discharge test measures the battery’s DC internal resistance. Increased internal resistance shows issues such as material aging, electrolyte depletion, and internal short circuit, which affect the battery’s charge efficiency.
- Charging Time. Record the time it takes to charge the battery from a low state to a full charge under battery load testing. Factors like a faulty charging circuit or slow chemical reaction within the battery contribute to longer charging times.
- Temperature. Normal battery temperature rises slowly under load conditions. However, rapid temperature rise indicates excessive internal resistance or potential safety risks.
Why are Battery Load Testing Results Important?
Battery load test results help assess battery health status, predict battery life and maintenance cycles, thereby ensuring battery safety.
Analysis results are an important basis for export certifications such as UN38.3 and IEC 62133. In the R&D phase, analyzing these results optimizes cell formulation, BMS strategies, and thermal management designs.
Conclusion
Battery load testing is an effective method to measure a battery’s voltage, capacity, and power capabilities. Apply various loads to the battery to simulate different operating conditions, discover battery defects, and further develop optimization strategies. Therefore, regularly inspecting the battery’s state of health by load test is essential.
FAQs about Battery Load Testing
How to load test a battery with a multimeter?
1. Make preparation. Ensure the multimeter is functioning. Select the right current measurement range based on the battery type.
2. Connect the multimeter in series between the battery and the load. First, disconnect the battery from the existing load. Then, connect the red test lead of the multimeter to the positive terminal of the battery and the black test lead to the positive terminal of the load.
3. Setting Up the Multimeter for Testing. Turn the multimeter dial to the DC range and select the appropriate range. Connect the circuit between the battery and the load.
4. Analyzing the Results. The current drawn by the battery under load matches the rated current of the load under normal conditions.
Are battery load testers worth it?
A battery load tester is a tool worth investing in if battery performance testing is a regular part of your work, or you have a high pursuit of performance optimization of electronic devices. Otherwise, you choose a basic testing method based on your needs if the test accuracy needs are not high.