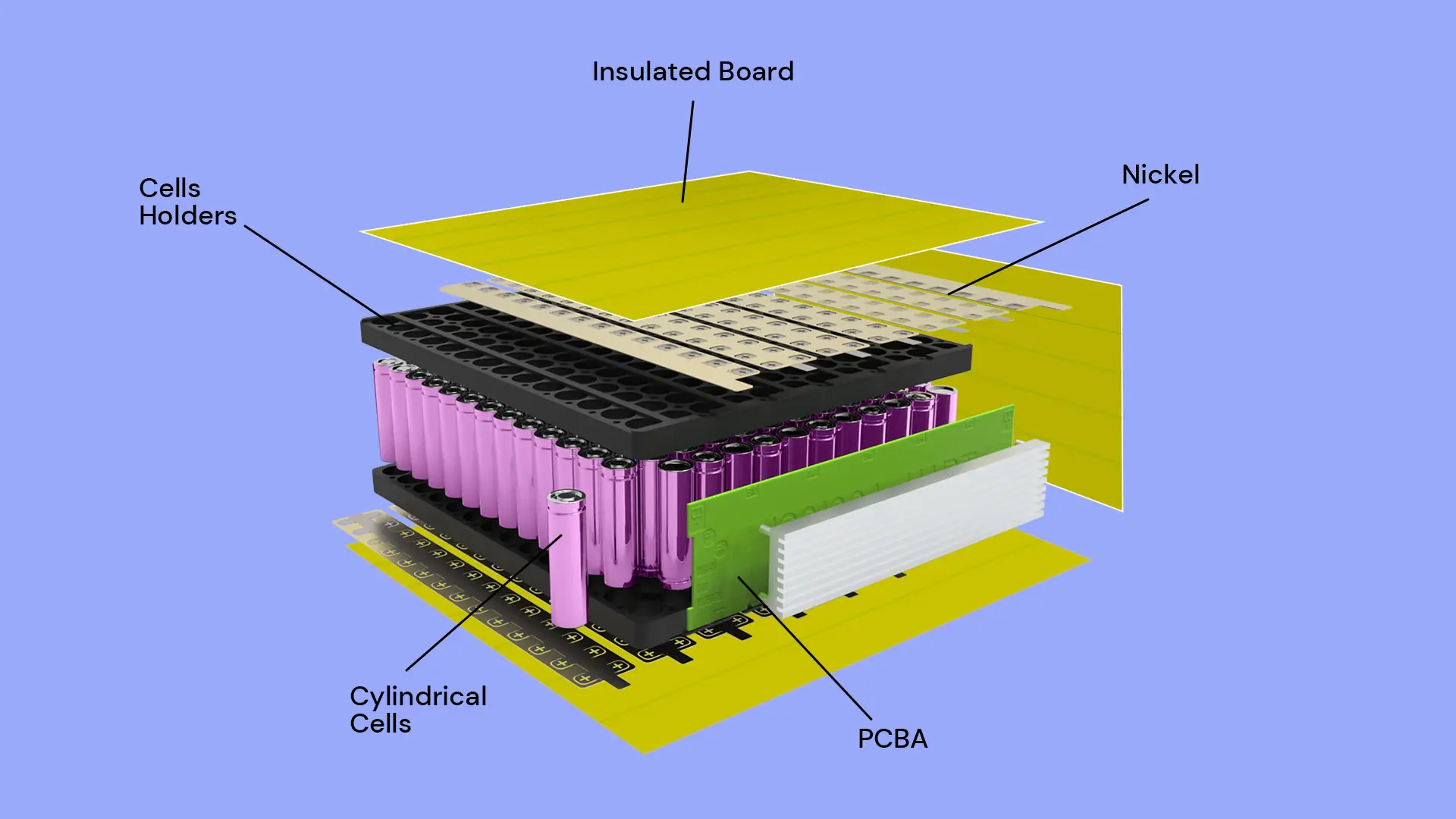
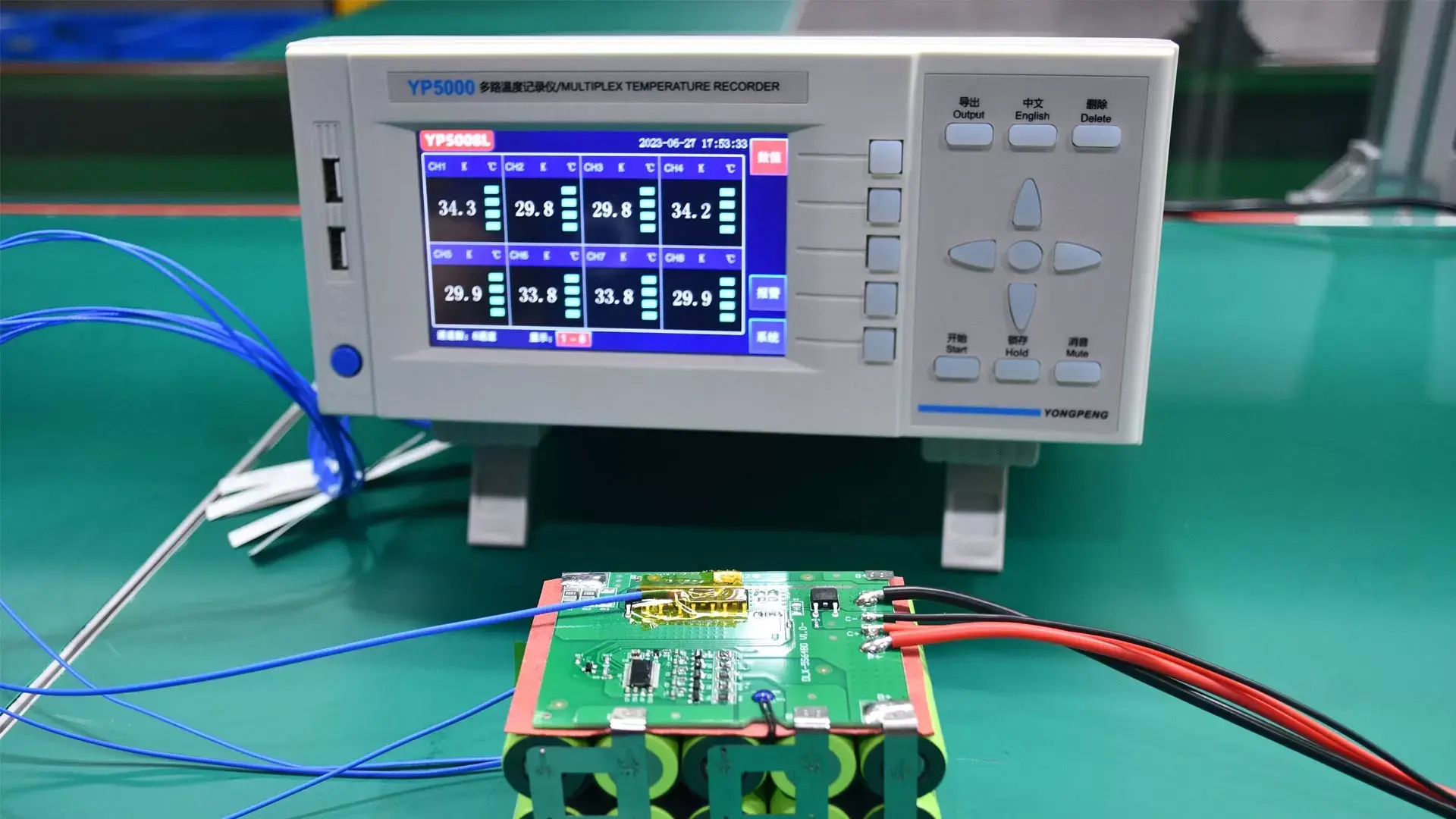
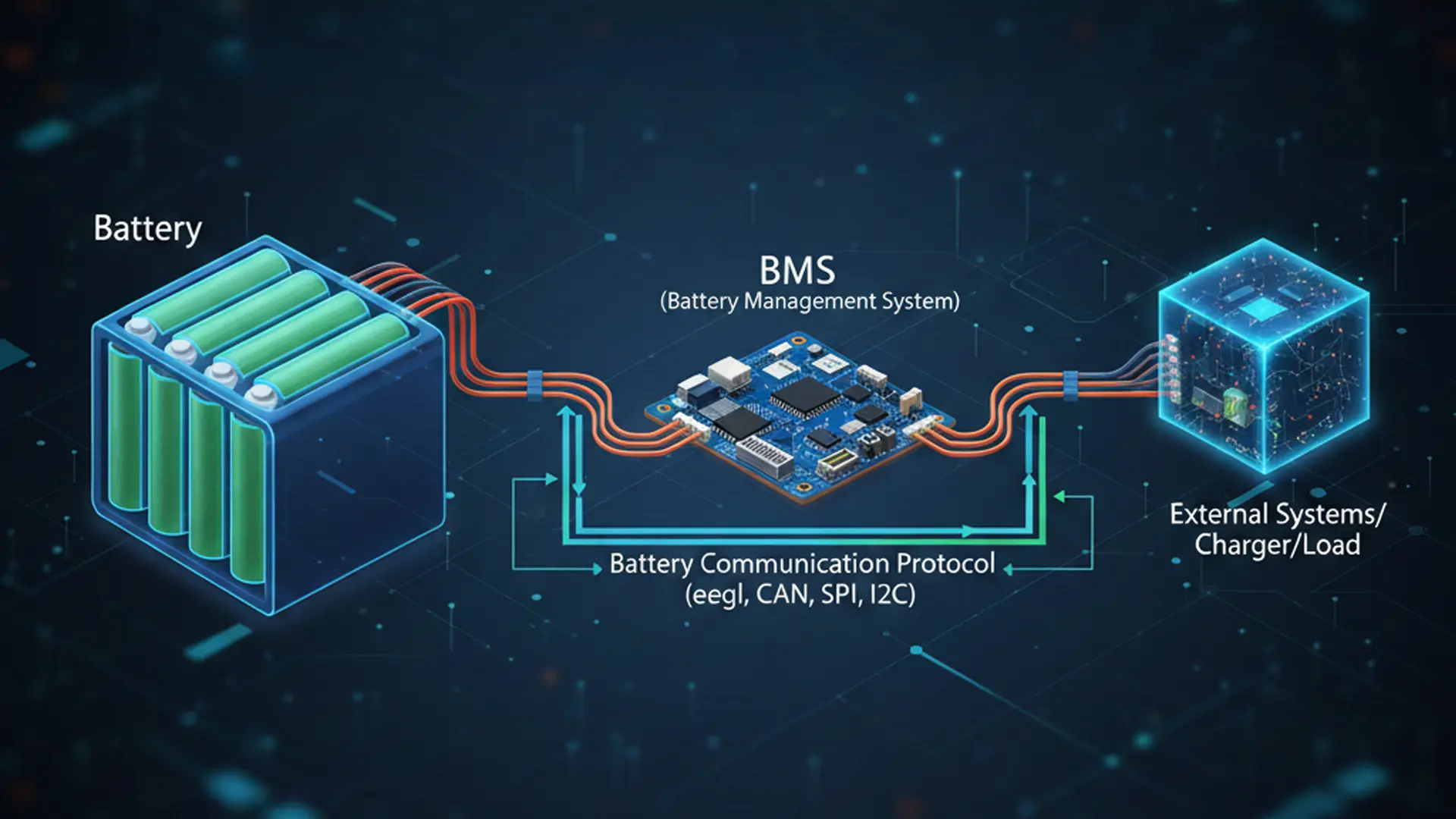
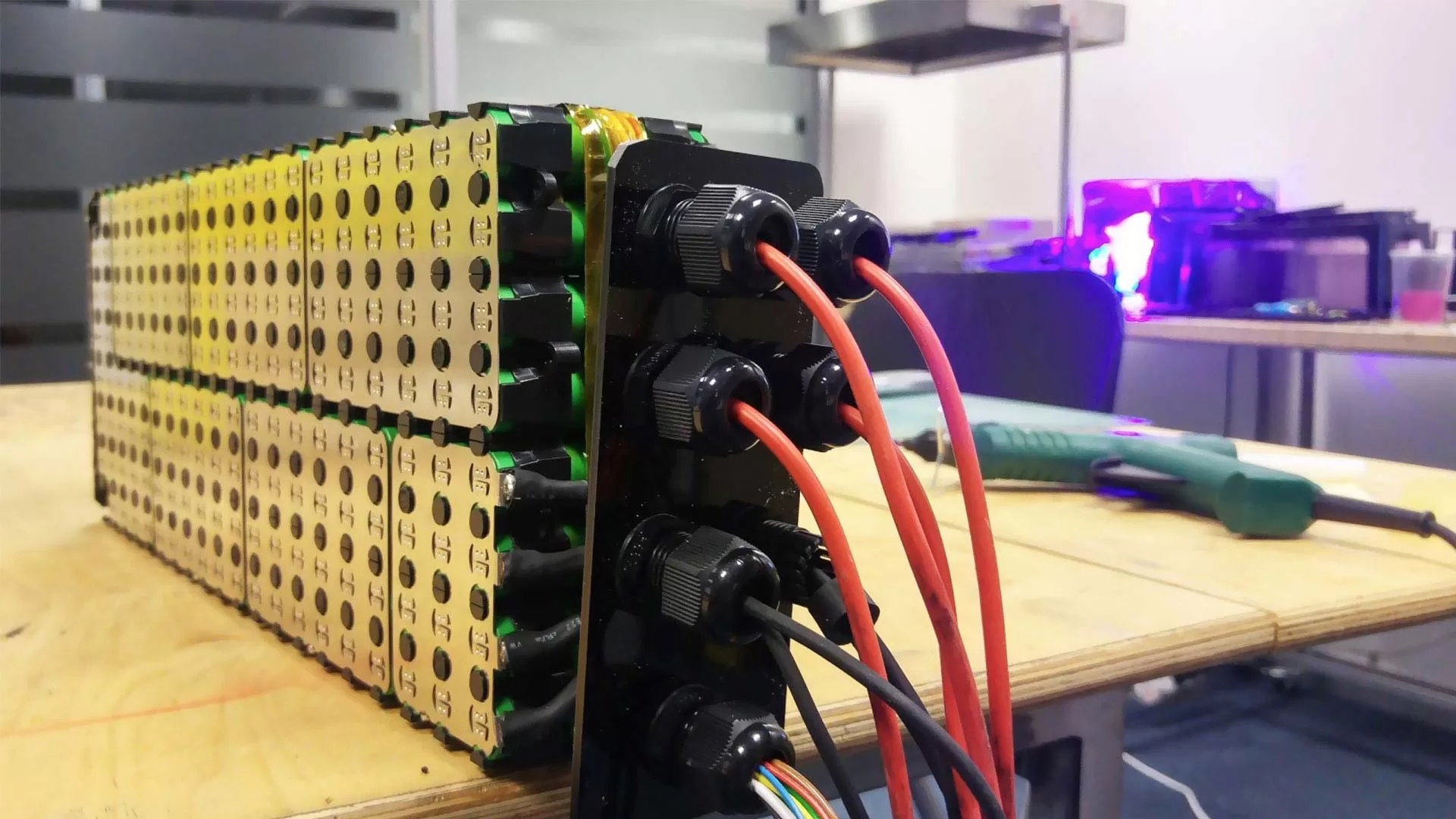
Battery enclosure design is a critical pillar of system engineering when manufacturing custom battery packs. Beyond simply shielding cells from physical damage, a well-engineered battery housing ensures long-term safety, reliability, and peak performance in demanding environments. From precise material selection and IP-rated waterproofing to complex thermal management and regulatory compliance, every detail impacts the balance between energy density and structural integrity. This article explores more design details to help engineers select appropriate custom battery enclosure.
Battery Enclosure Design Purpose and Function
Mechanical Protection. Battery casing withstand external impacts, vibrations, and compression to protect the internal battery components from damage.
Sealing Protection. Battery enclosure IP67/IP68 protection rating to prevents moisture, dust, and chemicals from entering the battery, avoiding short circuits.
Thermal Management. Assists in battery heat dissipation, maintaining the battery operating temperature within reasonable range to prevent overheating that could lead to performance degradation.
Insulation and Electrical Safety. Ensures insulation between the casing and the internal battery electrodes to prevent leakage and electric shock accidents.
Lightweight Design. Manufacture light battery pack casing to enhance battery energy density while meet strength and functional requirements.
Battery Enclosure Material Selection
In traditional battery enclosure designs, common materials include steel plates, plastic and aluminum alloys, offering rugged mechanical strength and mature manufacturing processes, ideal for mass production. They apply protective coating to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics in marine, humid and high-temperature conditions.
However, energy efficiency, environmental protection, lightweight construction drive diverse battery enclosure materials, such as carbon fiber composites, PA6 (nylon materials), aluminum, and steel. Here we introduce the features and application of battery pack enclosure design materials.
PVC Battery Housing
PVC(polyvinyl chloride) casing is one of the popular plastic battery enclosure due to its affordability and portability. It often used in temporary protective and basic packaging of lithium-ion battery pack. PVC heat sealing suits lightweight packs with few series and parallel cells. For battery packs weighing ≥1kg, adding fixed bracket needs between the cells with fiberglass sheet protection before applying PVC heat sealing.

Cons
- Limited heat resistance. The pure PVC does not exceed 60°C at long-term temperature environment. Modification and the addition of heat stabilizers improves its heat resistance.
- Low-temperature brittleness. PVC is prone to becoming brittle, and its impact resistance decreases. Adding toughening agents and using blending modification methods for enhanced performance.
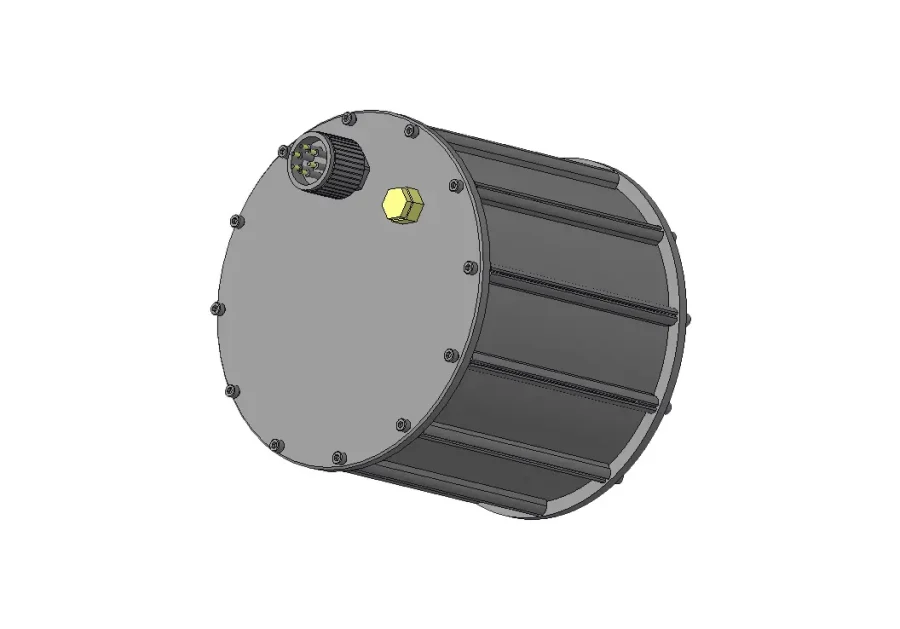
Aluminum Alloy Battery Enclosure
The aluminum alloy enclosure is a common metal battery enclosure and features with lightweight, high thermal conductivity and extensibility. Anodizing increases its oxide layer on the aluminum surface and improves corrosion resistance, wear resistance and aesthetics, while painting enhances the casing durability.
Pros
- Lightweight. Aluminum alloy battery enclosures have a density of 2.7 g/cm³, just one-third that of steel (7.8 g/cm³). This reduces the battery weight, enhances energy density, and helps extend both range and portability.
- High Thermal Conductivity. It has high thermal conductivity(about 237 W/(m·K)), which allows efficient heat transfer and prevents overheating, improving the battery’s cycle life.
- Easy to Process and Form. It has excellent ductility and can be molded into various shapes for battery enclosures through extrusion, stamping, die-casting and CNC, reducing production cycle.
- Strong Corrosion Resistance. Aluminum alloys form dense aluminum oxide film on the surface, which maintains stability in humid, marine and high temperature environments.

Cons
- Lower strength. Aluminum alloy has lower strength and hardness compared to steel. It requires reinforced structures to ensure safety when encounters extrusion and impact.
- High Cost. Aluminum alloy materials are expensive, and precise CNC machining process, which involves computer-controlled systems and skilled labor, adds to the overall manufacturing cost.
Application
- Portable Device Batteries. Aluminum alloy battery casing boasts lightweight design for laptops and smartphones
- Energy Storage Batteries. Aluminum alloy battery casings shines for durability and heat dissipation advantages.
Types
- The 3003 aluminum manganese alloy offers long lifespan, durability and easy to welding for stamped components of battery enclosures, such as battery covers, side panels. CATL uses “7-series aluminum” for the lower battery box.
- The 6061 and 6063 are aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloys, known for their high strength and great corrosion resistance. They can be shaped into profiles through extrusion and are used for structural components such as frames, borders, and bottom plates of battery enclosures.
Steel Battery Enclosure
The steel battery enclosure is made by welding cast steel plates, which is economical battery metal casing material for mass production. Steel casings offer merits such as high strength, good safety and high cost-effectiveness. It requires anti-corrosion treatment to ensure stability under high-temperature conditions.
Advantage:
- High Rigidity. Steel features with high strength and high safety, resisting external impacts, collisions, and compression, providing reliable physical protection for reducing battery damage risk.
- Superior Corrosion Resistance. Steel enclosure resist electrolyte corrosion and external environmental erosion with galvanizing, aluminum plating, extending the battery’s lifespan.
- Cost-effectiveness. Steel is inexpensive, and its processing technology is mature, making costs controllable during large-scale production.
Disadvantage:
- Heavy weight. High density steel results in heavier battery casing, which affects portability and runtime.
- Poor thermal conductivity. Steel battery enclosure features with internal low thermal conductivity(about 45W/(m·K)), which limits battery heat transfer. Additional cooling systems contributes to increases complexity and cost.
Application:
- Industrial Equipment Batteries. Forklifts, electric pallet trucks need steel battery enclosure to provides robust protection.
- Electric vehicles. Steel battery pack casings are used as frame structure to balance cost, safety, and lightweight requirements.
Safety and Regulation Consideration
Sealing and Connection Design
- Sealing Design. Lithium battery sealed enclosure uses sealing materials such as gaskets, sealants, and O-rings to ensure the airtightness of the enclosure. The sealing surface design must ensure uniform clamping force to prevent leakage. Conduct battery enclosure leak test for enhanced safety.
- Connection Method. Maintain reliable enclosure and battery module and internal components connection. Common connection methods include welding, such as friction stir welding, MIG welding, bolted connections, and riveting.
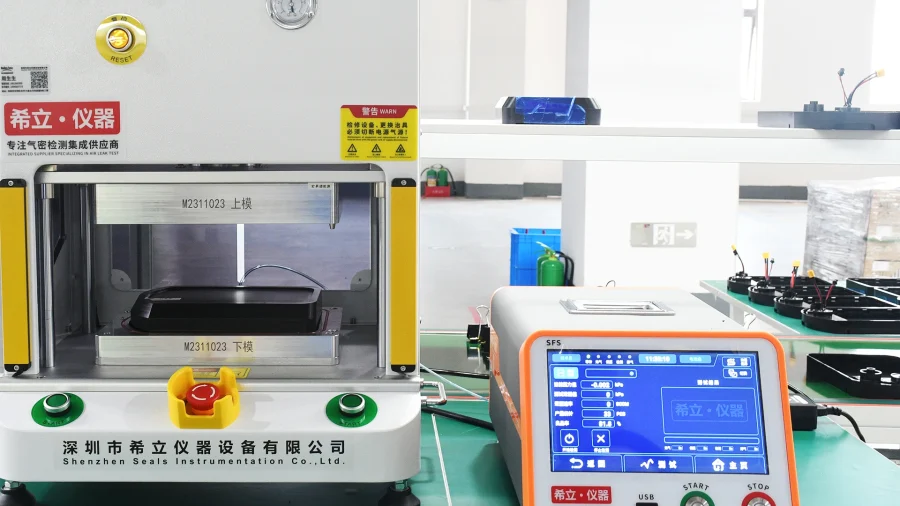
Leak Test Battery Enclosures
Air leak testing and immersion(water ingress) testing are two major lithium battery pack enclosure airtightness testing for manufacturing.
During the air leak test, the battery enclosure cover is sealed, leaving only a connector port as the air inlet. Apply controlled air pressure and monitoring for any pressure loss or air leakage to evaluate airtightness. For immersion test, the entire battery enclosure is submerged in water, and the enclosure’s airtightness is assessed by checking whether water has entered the interior.

Battery Enclosure Fire Protection Design
- Explosion Protection and Pressure Relief. Incorporate pressure relief devices, such as safety valves and rupture discs, to prevent explosions caused by excessive internal pressure within the battery.
- Thermal Runaway Protection. Thermoplastic materials, long-glass fiber materials, flame-retardant materials stands up high temperature compared with steel and aluminum, reducing cost and accelerating manufacturing. Utilizes insulation layers and thermal diffusion barriers to slow the spread of thermal runaway.
- Using thermal management materials such as phase change materials (PCM), heat pipes, and heat sinks, and employing thermal simulation analysis, engineers predict the heat dissipation of the battery enclosure. Construct air and cooling system, based on cell arrangement at design phrase to optimize internal airflow and improves heat dissipation.
Waterproof Battery Enclosure Design
Ingress Protection(IP) ratings, as defined by IEC60529, refers to the enclosure ability’s to block water and dust in strong ultraviolet radiation, high humidity and salt spray conditions. It affects battery enclosure’s safety, reliability and lifespan.

Battery Enclosure Ingress Protection Level
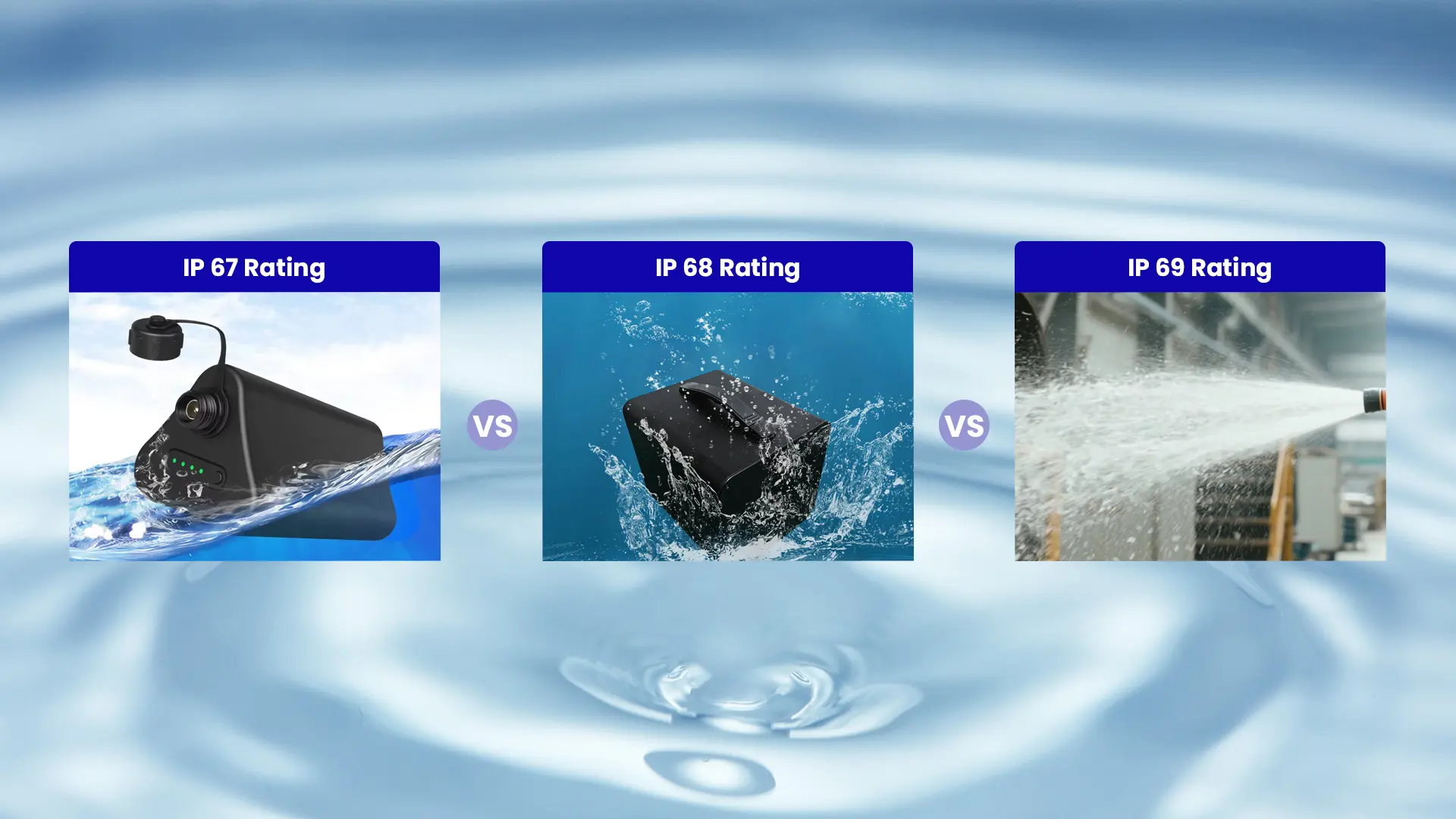
The battery pack enclosure design in ingress protection hinges on your detailed requirement. IP6X means fully dust-proof protection. IP67 rating withstands 1 meter immersion up to 30 minutes, IP68-rated reaches continuous submersion in 1–100 meters of water for up to 5 hours and IP69-rated resists high pressure water jet at high temperature.
| Technical Requirement | IP67 | IP68 | IP69K |
| Standard | IEC 60529 | IEC 60529 | DIN 40050-9 |
| Application | Portable devices exposed to water in short period | Marine equipment, ROV, yacht for prolonged submersion | Industrial machinery for high-pressure water jet cleaning |
| Challenges | Material corrodes in short-term humidityPressure changes lead to water ingress | Long-term immersion affects enclosure’s sealingSealed enclosure balances heat dissipation and waterproof | High-pressure water jet deforms enclosure. High-temperature water flow affects material stability |
Here we write an IP rating waterproof battery guide to explore features, test standard and application in different protection level.
Waterproof Enclosure Battery Pack Design Technology
Battery Enclosure Sealing Structure Design
- Flange and Sealing Gasket Design. Upper and lower enclosures adopt bent flange structure, with sealing gasket compressed by tightening bolts. Sealing gasket have effective sealing width and compression rate is between 30%-70% to balance sealing effect and material durability.
- Connector Sealing Design. Adding sealing glue and gaskets at connector interface and fixing high-low pressure connector to enclosure using blind hole welding nuts are two effective ways for enhance connector sealing.
- Use platform welding nut for the exhaust valve and explosion-proof valve, ensuring nut surface is flush with enclosure surface and the sealing between valve body and enclosure.
Material Selection
- Rubber Sealing Gaskets. Selecting rubber materials with good aging resistance, high and low-temperature resistance, and waterproof performance, such as EPDM rubber and silicone rubber [Fictiv, Waterproof Enclosure Design 101].
- Foam Sealing Materials. Using foam silicone, foam rubber with good elasticity and compression recovery, which form seals through compression. Control the foam’s thickness, density, and compression ratio.
- Using structural adhesives and sealants to fill the gaps in the enclosure weld seams and connector interfaces.
Battery Enclosure Test and Verification
IP67 and IP68 Testing
- Submersion Test. Battery pack is submerged in water at depth of 1 meter for 30 minutes(IP67) and 24 hours(IP68) to check for enclosure water ingress. Then, take insulation resistance tests to ensure its electrical performance.
- Gas Test Method. Pressurize the sealed enclosure to certain level (e.g., 10kPa) and upholds over 1 minute. Use soap water is used to check for leaks.
IP69K Testing
- High-Temperature and Pressure Spray Test. Using spray device to spray water at specific pressures(e.g.,100 bar) and angles to simulate extreme conditions.
Fabricate Battery Enclosure Design Guidelines
- Step1. Decide your battery enclosure design requirement. Engineers use CAD software to build custom battery casing modeling, determining battery enclosure dimensions and shape. Then, combine Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to analyze enclosure stress distribution under mechanical load such as vibration, shock, boasting prototyping.
- Step2. Select metal sheets or tubes for the battery box. Battery casings utilizes aluminum-magnesium alloys, plastic, and carbon fiber composite materials to enhances mechanical protection against impacts, collisions or compression.
- Step3. Forming and Machining. Stamping and Deep Drawing. Metal sheets are stamped drawn using molds to form the basic enclosure shapes, such as prismatic and cylindrical. The stamping process requires precise control of mold accuracy to ensure dimensional consistency and surface flatness enclosure. Bending and Folding. Press brakes are used to bend metal sheets to meet design requirements for enclosures with complex geometries.
- Step4. Welding and Assembly. Stamped enclosure components are joined into complete structure through welding processes. Welding methods include laser welding, soldering, brazing, adhesive bonding, bolts. Install enclosure accessory like top covers, explosion-proof valves, and terminals to ensure all components are securely mounted.

- Step5. Surface Treatment. Require surface treatment to improve casing corrosion resistance, involving anodizing(aluminum casings), electroplating (steel casings), and applying corrosion-resistant coating.
- Step6. Quality Inspection. Use measuring tools, such as calipers, micrometers to check the housing dimensional accuracy. Then, Verifying battery enclosure’s sealing performance through air leak testing and water pressure testing method to prevent electrolyte leakage.
- Step7. Battery Enclosure Branding and Aesthetic Customization. Use laser etching, label and digital logo printing for manufacturing custom markings and warnings in battery enclosure. It helps with boasting your brand identity in your targeted market for enhance your competitiveness.
Battery Housing Manufacturing with Packaging Types
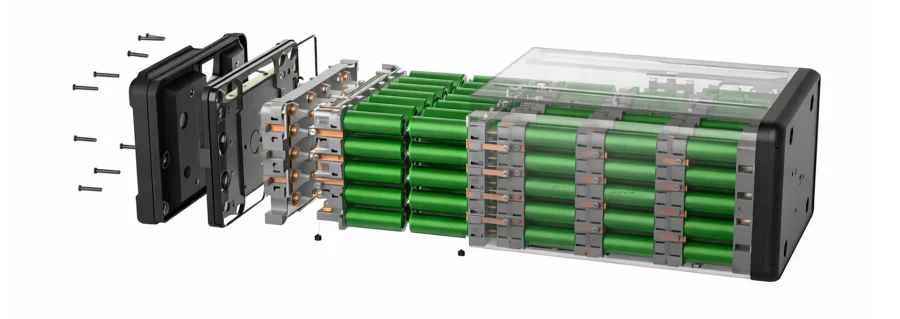
Prismatic Battery Housing Manufacturing
The prismatic lithium battery housings are made of metal materials, such as aluminum alloy and stainless steel. Its manufacturing process involves stamping and deep drawing, where metal sheets are formed into enclosures with specific shapes and dimensions using molds. The stamping process requires high mold precision to ensure dimensional consistency and surface flatness of the enclosure, which is critical for the assembly of internal battery components. The deep drawing process shapes the depth and form of the enclosure, allowing it to accommodate the battery cells.
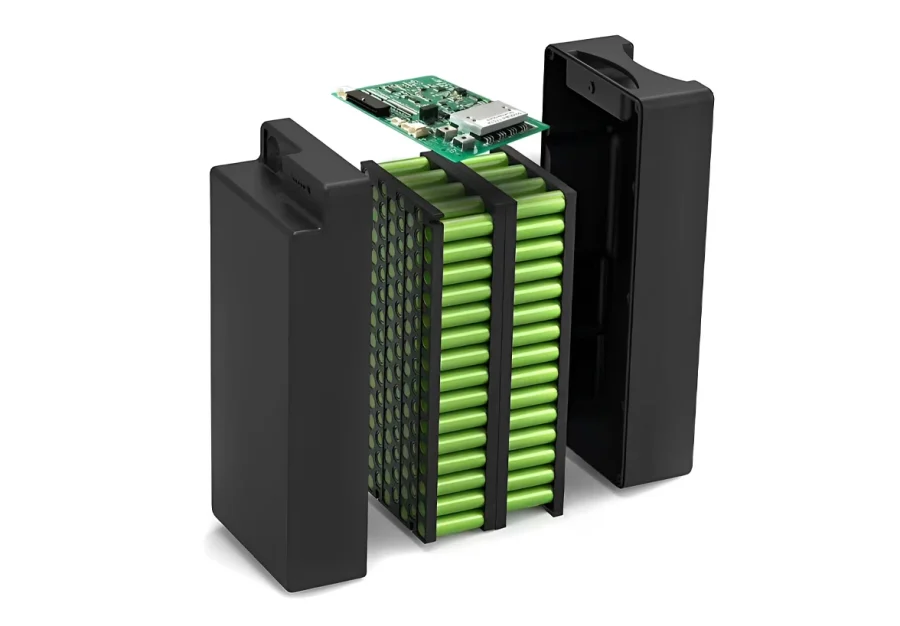
Cylindrical Lithium Battery Housing Manufacturing
The cylindrical housing are made of metal and use seamless steel tube drawing process. Metal tubes are stretched in specialized molds to form cylindrical enclosures with specific wall thicknesses and lengths. During the drawing process, the material properties of the tube, drawing speed, and mold lubrication must be precisely controlled to ensure dimensional accuracy and surface quality. Compared to prismatic battery enclosure manufacturing, cylindrical enclosure production is simpler and has higher production efficiency.

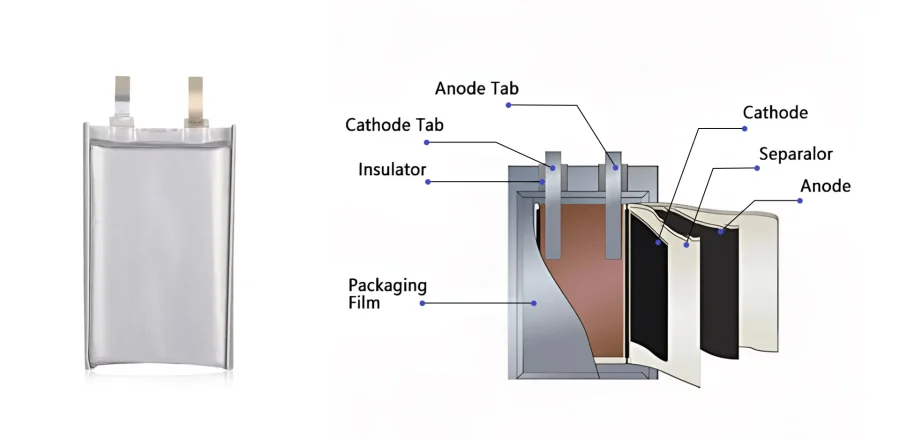
Pouch (Soft Pack) Battery Housing Manufacturing
Pouch housing are manufactured with aluminum-plastic composite films material, which combine the barrier properties of metal with the flexibility of plastic. The pouch structure allows batteries to be custom-designed for wearable devices, such as ultra-thin and irregular shapes. The aluminum-plastic film can bulge and rupture when internal pressure becomes high, releasing pressure to prevent serious incidents such as explosions.
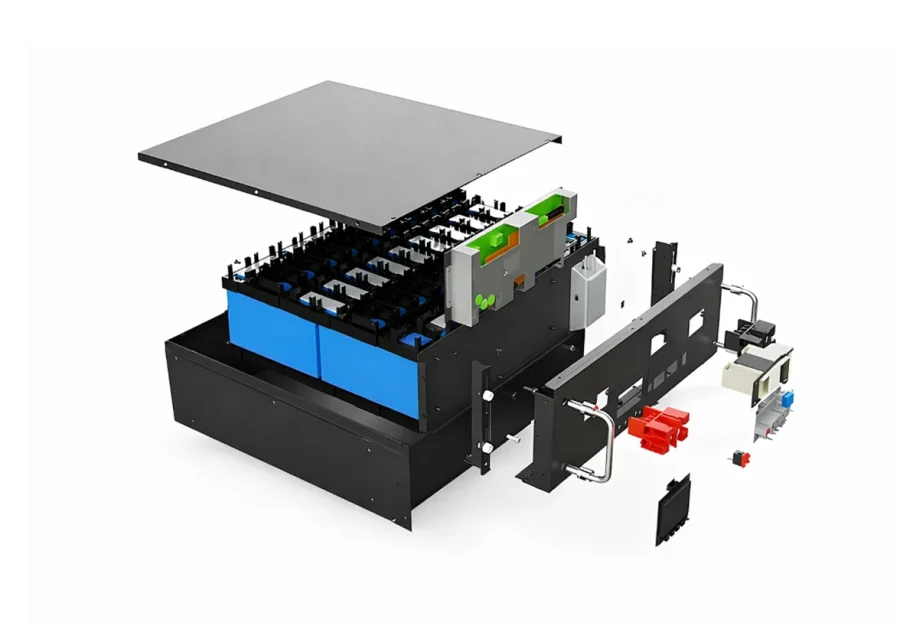
Application of Battery Enclosure Design
Various application involves different enclosure design requirements. Here our engineering teams conclude major design considerations.
Marine Battery Enclosure
ROV (Remotely Operated Vehicle) ,electric surfboard and electric boats battery pack operates in low temperature marine environments.
- Sealing and waterproofing requirement. Marine battery casings need to meet IP67/ IP68 protection rating to prevent moisture and dust from entering the battery. Then adopt sealing rings and waterproof coatings for marine battery housing.
- Salt Spray Corrosion Resistance. 316 stainless steel, aluminum alloy, or corrosion-resistant composite materials prevent salt spray corrosion from causing rusting and deterioration of the casing.
Outdoor Battery Enclosure Box
- Extreme Temperature Resistance. Outdoor environments experience vast temperature fluctuations(-40°C to 85°C). Thus, Battery enclosure materials maintain mechanical property to prevent material deformation and cracking.
- UV Protection. Outdoor battery-powered cameras are exposed to sunlight, and their housing materials are affected by ultraviolet radiation, leading to aging, discoloration, and embrittlement. Therefore, using materials with UV resistance is crucial for extending the lifespan of the camera housing.
Battery Enclosure for Electric Skateboard
- Lightweight Design. Lightweight housing helps improve the skateboard’s range and handling performance. Prioritize materials with low density, such as aluminum alloys, carbon fiber composites, or high-performance plastics.
- Strength and Stiffness. The casing withstand vibrations, impacts, and potential collision forces during skateboard operation. Rugged materials and reinforcing structural design enhance casing’s resistance to deformation, such as adding ribs or frames.
Conclusion
As battery technologies evolve toward higher energy densities, the demands on housing—particularly regarding thermal runaway mitigation and precise sealing—will only increase. By integrating these design guidelines early in your development cycle, you ensure a product that is not only high-performing but also fully compliant with global safety standards. For your next project, choosing a manufacturing partner who understands these intricacies is the final, and perhaps most crucial, step in bringing a reliable power solution to market.
For further detailed suggestion, please consult our professional engineer team for customizing battery enclosure solution.
FAQs about Battery Enclosure Design
Where can l find manufacturers specializing in custom plastic battery housings?
Custom plastic enclosure design involves material selection, mold design, injection molding processes, and sealing structure design. Simply finding supplier carries risks such as insufficient technical support and incomplete testing and validation. CM Batteries is battery pack suppliers that provides integrated services. We manufacture lithium battery packs based on specifications but also design enclosure solutions that meet safety, thermal management, mechanical strength requirements.
What are the critical thermal management strategies for battery pack enclosures?
First, Using enclosure materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum alloys and carbon fiber composites. It transfers heat generated by the battery to the enclosure surface through natural convection or forced cooling.
Second, add thermal insulation layers to the interior or exterior of the battery enclosure to reduce heat exchange between the battery and the external environment, such as aerogels or ceramic silicone materials.
Third, integrate battery enclosure with heat dissipation. Cooling channels embedded in the enclosure can be in close contact with battery modules, allowing circulating coolant. Air cooling fins help guide airflow through the battery pack.
According to recent studies published in Energy Storage Materials, integrate Phase Change Material (PCM) with battery pack enclosure to maintain temperature stability, such as paraffin-based PCMs. As battery temperature rises, the PCM absorbs heat and undergoes phase change to store thermal energy. When temperature decreases, the PCM releases the stored heat.
Fifth, Temperature sensors are installed on the battery pack casing to monitor battery temperature in real time and feed the data back to the battery management system (BMS). Then BMS adjusts the cooling heating operation, such as controlling the fan speed, coolant flow rate, and heating element power.
Why do we need ventilation in a battery enclosure?
First, Ventilation is crucial for heat dissipation, facilitating air circulation to remove the heat generated during battery charging and discharging. This avoids shortened lifespan and thermal runaway. Second, Ventilation prevents corrosion and moisture damage. It keeps the air around the battery dry, reducing moisture accumulation and preventing corrosion of the battery casing and connecting components. Third, ventilation helps maintain stable temperature and humidity, ensuring uniform battery chemical reactions.