Based on how they are built and programmed, autonomous mobile robots can do many different jobs, such as moving and inspecting materials and helping with logistics in places like hospitals, factories, and warehouses. They can move things, keep track of inventory, help with healthcare, clean and fix things, and do specialty tasks like painting or welding. As technology improves and new uses appear, these robots’ jobs keep growing. This makes it more important that their batteries work well.
However, heat dissipation, space constraints, insufficient runtime, thermal management challenges are main battery design difficulties that prey on many manufacturers’ mind. Thus, custom batteries tailored to the power requirements of different AMRs have become a key solution.
Let’s delves into this articles to find in-depth analysis for AMR lithium battery designing.
How Market Trends Drives the Demand of AMR Lithium Battery?
Global Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) market is experiencing rapid rapid expansion. Booming e-commerce sector, labor shortages, Industry 4.0 initiatives, artificial intelligence advance, the widespread of Robots as a Service (RAAS) drives more companies are deploying AMRs for 24/7 material handling and production line collaboration. Batteries become key component of the cost and performance of AMR systems.

Table1. AMRs market trends drive battery technology
| AMRs Market/Technology Trends | Requirements for AMR Batteries | Specific Reasons |
| 24/7 Automated Operation | Longer endurance and low degradation | Opportunity charging and shallow charge/discharge cycles are common, as AMRs require multiple charges and high durability. |
| AI Perception and High-Load Sensors | Higher power output, faster instantaneous response | LiDAR, 3D cameras, vision SLAM, and AI computing demand peak power . |
| Industrial-Grade Deployment | Strong thermal management, wide-temperature operation (-20°C to 60°C) | AMRs stay stable in harsh dusty areas, hot rooms. |
| Large-Scale AMR Fleet Operation | Smarter data and communication capabilities (SOC/SOH/temperature monitoring) | Real-time battery data is vital for fleet scheduling, predictive maintenance |
| Diverse AMR Form Factors and Operating Requirement | Need custom battery packs with different size, voltage, current, communication, protection | Different voltage, connectors, CAN/UART communication, and hot-swapping make them incompatible with off-the-shelf batteries. |
All these trend drive the demand of custom lithium iron phosphate (LFP), ternary lithium(NMC) and high-rate lithium polymer battery packs for autonomous mobile robots(AMRs). Compared to traditional solutions, modern AMRs place great emphasis on superior energy density, high power output, wide operating temperature range, safe design, and scalable platform-based battery packs.
Key Design Challenges for AMR Lithium Battery
Unlike traditional AGVs that follow fixed guidance tracks, Autonomous Mobile Robots(AMRs) operate in complex environments and require continuous, high-density, and reliable power to support navigation, sensing, computing, and motion control. This creates several unique challenges for battery design.
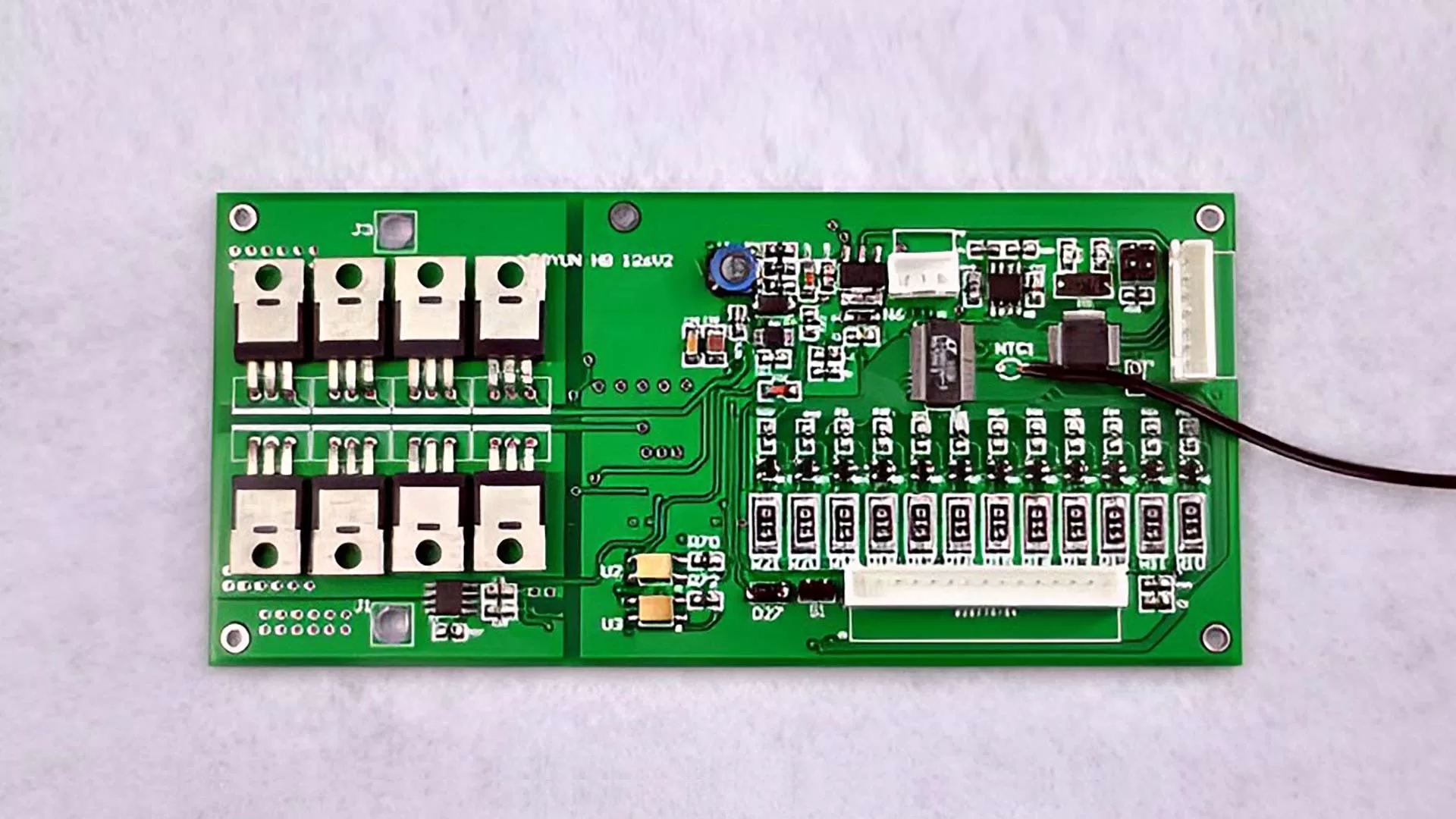
Battery Management System (BMS) Complexity
Autonomous Mobile Robot(AMR) has more complex battery management system(BMS) than consumer devices. AMR batteries integrate safety monitoring, energy consumption estimation, communication scheduling, and lifecycle tracking.
- Energy Prediction Challenge. Mobile robot battery requires BMS to estimate high-precision SOC/SOE under shallow charge/discharge, avoiding mission interruption or return failure to the charging station.
- High Load Variability. AMR batteries experience large instantaneous current fluctuations during startup, turning, and lifting, requiring precise current, voltage, and temperature protection from the BMS.
- Communication Integration Difficulty. BMS must interface with multiple industrial communication protocols, including CAN, RS485, fleet/robot management systems (FMS/RMS), and host computers, ensuring reliable data exchange and task coordination.
- Lacks Unified Standard. Each AMR battery requires different protocols, structure and voltage platform, which increases BMS custom development complexity.
Harsh Thermal Management Challenges
AMRs work in high-temperature warehouses, cold-chain storage(-20℃ to -30℃), high-load industrial lines and constrained spaces with poor ventilation, which poses extreme temperature challenges for autonomous mobile robot lithium battery.
- Extreme Temperature Accelerates Battery Aging. High temperatures increase chemical reactions rate inside the AMR battery and reduces capacity while low temperatures slow down ion movement and reduce electrolyte conductivity, decreasing efficiency.
- Voltage Imbalance and SOC Miscalculation. Temperature fluctuations cause voltage imbalance across cells, leading to inaccurate state-of-charge (SOC) readings and potential AMR failures.
- Cell Swelling and Over-temperature Shutdowns. High temperatures and rapid cooling lead to cell swelling, triggering safety shutdowns and halting AMR operations.
Energy Capacity and Endurance
AMRs need long-lasting operation in warehouses, logistics centers, production lines. Heavy task scheduling, throughput, and work efficiency place heavy demand on battery endurance. Traditional lead-acid and nickel-cadmium batteries with low energy density, large size, heavy weight, and limited cycle life, fail to provide sufficient runtime. As a result, autonomous mobile robot lithium battery experience frequent downtime for recharging, reduced operational efficiency, and potential disruption to automated workflows.
Power and Instantaneous Load Management
Autonomous mobile robot experience frequent and rapid load changes when accelerate, brake, lift goods, and perform steering corrections. These operation generate sudden spikes in current demand, posing great challenges for battery packs.
- High Instantaneous Current Requirements. AMRs batteries need to deliver large bursts of current during dynamic operations.
- Voltage Stability. Rapid load changes cause battery voltage drops, risking AMR mission interruption and system faults.
- Thermal and Mechanical stress. Advanced AMR requires AI-based decision-making and cloud data exchange, which generate high currents. It leads to heating in MOSFETs, busbars, and connectors, increasing the risk of component failure.
Modularity and Scalability Challenge
Diverse Autonomous Mobile Robots(AMRs) cover from light-duty service robots to heavy industrial AMRs for pallet handling, lifting, and towing. Therefore, AMR battery must offer high degree of scalability because of various mechanical structure, payload, and duty cycles.
- Multi-model Compatibility Requirement. Autonomous mobile robot industry lacks unified standards, so engineers must employ independent designs for installation space, layout, interface structure, and voltage platforms vary from 24V to 72V. It increases development costs and delivery cycles.
- Complexity of Split-Type Master-Slave Battery Packs. They place demand on accurate SOC, consistent current distribution and dynamic balancing control, synchronous triggering of over-current and over-temperature protection and bidirectional communication coordination in split or parallel structures.
- Hot Swapping Structure Brings Interface and safety challenges. It poses stress on BMS, power devices and connectors durability. A handshaking protocol is vital to prevent sparks and arcing.
- Complexity of Multi-Domain Management with Dual Voltage Outputs (e.g., 48V + 12V). Many AMR lithium batteries power the drive motor(high voltage domain) and control system and sensors(low voltage domain), thus requiring batteries with dual voltage outputs. It needs strict electrical isolation, stable low-voltage power supply and redundant control.
Basic Design Technologies for AMR Lithium Battery
Battery Cell Chemistry Selection
Choosing the right cell system is the cornerstone to manufacturing the advanced performance, lifespan, safety, and cost of AMR batteries. Different autonomous mobile robots have different requirements for energy density, thermal stability and cost.
- Lithium iron phosphate(LFP) batteries are utilized in most industrial warehouse AMRs due to excellent cycle life, thermal stability, and intrinsic safety, making them ideal for frequent scheduling and automated warehouse environments.
- Ternary lithium (NMC) batteries offer higher energy density and lighter weight, resulting in longer battery life and more compact structural designs for small and lightweight medical autonomous mobile robots.
- Sodium-ion batteries are beginning to enter cold chain logistics and large-scale cost-sensitive robotic projects. They offer vast advantages in low-temperature performance, safety, and cost structure, making them a potential complement to LFP.
- In future applications, solid-state batteries are expected to play a critical role in medical robots, precision service robots with high safety requirements—their ultra-high safety and higher energy density provide new direction for high-end AMR products.
| Chemistry | Advantages | limitations | Suitable Applications |
| LifePO4 Battery(LFP) | Long cycle life, superior thermal stability | Lower energy density | Warehouses, factory and logistics AMRs |
| Ternary Lithium Battery(NMC) | High energy density, lightweight design | High cost, lower intrinsic safety | Small AMRs, medical robots |
| Sodium-Ion Battery | Good low-temperature performance, cost-effective | Bulky volume | Cold-chain logistics AMRs, cost-sensitive AMRs |
| Solid-State Battery | Upgrated safety, wide-temperature performance | Limited commercial availability | Medical and aerospace-grade AMRs |
Table2. Battery Cell Chemistry Selection for Autonomous Mobile Robots(AMRs)

Electrical Architecture
Electrical architecture determines the power output, charging efficiency, and battery management capabilities of the AMR battery system. AMRs are equipped with wide range of sensors, including cameras, LiDAR, ultrasonic sensors, and IMUs, requiring battery to offer stable, low-noise, high-power output to support data processing and SLAM calculations.
- High Discharge Rate Cells (10C-20C). Support the instantaneous power demands of AMR under high loads.
- DC-DC Conversion. It ensures efficient battery operation under varying loads and reduces energy loss.
- Fast charging capability. Fast charging (1-2C) is a crucial component of AMR battery system design, especially for AMR applications requiring frequent charging.
Mechanical and Structural Design
Mechanical design involves shell material, installation method, and structural strength. AMR batteries need to be customized based on robot design, such as L-shaped, U-shaped, and flat structures, to maximize space utilization and ensure the battery pack stability.
- High-strength shell casing. Mobile robot battery pack utilizes aluminum or PC-ABS casing to enhance shock and drop resistance.
- Modular design. It facilitates autonomous mobile robot lithium battery pack maintenance and replacement, especially for quick-swap battery systems.
- IP67–IP68 waterproof and dust-proof rating housing. It allows AMRs expand into outdoor, food processing, cold chain, and humid supply chain applications .
Thermal Path Design
Thermal management is critical in AMR battery design, especially in high-power discharge and fast-charging conditions. AMR batteries generate lots of heat under high loads and high temperatures.
- Thermal conductive materials and heat sinks. Optimize heat dissipation to ensure heat distribution within the battery pack.
- Temperature control system. Includes power temperature controller (PTC) or thermal insulation film for low-temperature start-up, ensuring stable operation in cold environments.
- Fireproof and thermal insulation design. Employs thermal runaway protection structure to prevent fires caused by short circuits or battery overheating.
Communication & System Integration
AMR battery systems require real-time communication with robot control and scheduling systems, such as RMS/FMS to adjust battery status and optimize robot performance. Communication protocols employ industry standards such as CAN and RS485 to ensure reliable data transmission.
Our custom BMS support various communication protocols, and are compatible with common AMR control systems. To help engineering teams understand compatibility, this table summarizes the common communication protocols for AMR battery systems and applications.
Table3. Main AMR Lithium Battery Communication Protocols Overview
| Protocol | Type | Role in AMR Battery System | Why lt Matters |
| CAN (Controller Area Network) | Industrial bus | BMS – AMR main controller | Fast, stable, noise-resistant; the default protocol for most AMR |
| CAN FD | Industrial bus(enhanced) | High-speed status reporting, diagnostics, log upload | Higher bandwidth; ideal for high-performance AMRs and advanced BMS |
| RS485 | Industrial serial port | BMS – charger/ host computer/ warehouse system | Stable over long distances and cost-efficient; common for chargers and debugging |
| Modbus-RTU (based on RS485) | Industrial protocol | Standard data exchange between robot system and battery | Simple and highly compatible; Used in factory AMRs |
| BLE(Bluetooth Low Energy) | Wireless | Battery maintenance, mobile app reading, on-site debugging | Easy wireless access for maintenance; not for main control |
Safety and Certification
Battery safety design and international certifications are essential components for AMR lithium battery.
- Multi-layered Protection. Battery pack employs hardware redundancy design and is equipped with BMS software protection to ensure safe and stable operation under complex working conditions.
- International Certifications. IEC62619, IEC62133, and UN38.3 standards ensure battery safety during transportation, installation, and use. They are also critical for enterprises to broaden oversea market.
Table4. Battery certifications for AMR Lithium Battery
| Certification | Category | What It Ensures | Why It Matters for AMRs |
| UN 38.3 | Transportation Safety | Verifies battery safety during air/sea/land transport | Mandatory for global shipment |
| IEC 62133-2 | Cell & Pack Safety | Ensures safety of Li-ion cells /small/medium battery packs | Global safety standard; Required for medical and service AMR |
| IEC 62619 | Industrial Battery Safety | Tests for thermal protection,internal cell fault response, system-level protection | Standard for and industrial AMRs operating 24/7 |
| UL 2054 | Pack Safety(North America) | Evaluates shock, fire, and mechanical risks in battery packs | Essential for North American AMR deployment, especially medical and delivery robots |
| ISO 3691-4 | Robot System Safety | Defines AMR system safety, emergency stop behavior, safe stopping when battery faults | Ensures AMRs remain safe in human-robot shared environments |
| ISO 13849-1 / PL | Functional Safety | Defines safety levels for control systems and BMS protection chains | Required for safety AMR functions such as emergency braking, high-voltage control |
| IEC 61508 (SIL) | Functional Safety (Advanced) | Assesses software reliability, hardware fault tolerance | Needed for high-speed, medical, or high-risk AMRs with strict reliability |
We also write a complete guide to lithium-Ion battery pack certificate for exploring more detailed battery certifications information.
Advanced Design Technologies for AMR Lithium Battery
As robotics industry advances by leaps and bounds, AMR battery technology is evolving from traditional power system into an intelligent and modular robot power platform that has wide temperature range and high power.
Intelligent Battery Management System(BMS) Algorithms
The Battery Management System(BMS) technology for autonomous mobile robot lithium battery is far more complex, requiring the battery to possess energy system capability to improve prediction accuracy, reducing failures downtime, and support multi-robot collaborative scheduling, including:
- High-accuracy SOC and SOE Estimation. BMS monitors minimum error under shallow charge/discharge, rapid duty cycles. And varying loads ensure accurate runtime prediction.
- Real-time Load Identification. The BMS of mobile robot batteries adapt transient high currents during handling, acceleration, lifting, and adjusts protection and energy model.
- Intelligent Power Management (Wake-up / Sleep / Auto Fault-Clear). These BMS working modes reduce the standby power consumption of mobile battery while improving availability by recovering from minor faults.
Wide-Temperature Battery Technology
AMR batteries are used in environments with extreme temperature differences, such as cryogenic chambers, outdoor parks, and manufacturing workshops. Thus, the AMR lithium battery must have wide temperature range performance. Wide temperature battery technology is the core strength of CM Batteries with supporting -40℃~+85℃ temperature ranges. It ensures that the AMR maintains stable battery life without losing tasks, experiencing data loss, and crashing.
Additionally, active thermal management. Heating film, thermal compensation loops and low-temperature activation. Utilizes PID temperature control, preheating strategies, insulation structures, and thermal conduction materials to restore power in low temperatures and prevent thermal imbalance.
Hot-Swapping Battery Technology
The hot-swapping battery technology is a mission-critical requirement for 24/7 warehouse and logistics AMRs requirement, which ensures minimal downtime and eliminates charging wait time and lower total cost of ownership(TCO).
- Zero-Downtime Operation for Autonomous Mobile Robot. Hot-swappable robot battery modules allow replacement and capacity expansion without shutting down. Spark-free hot-plug architecture with pre-charge circuits and handshake protocols prevent inrush current, arc damage, and controller reboot.
- Enhanced AMR System Safety and Reliability. Redundant power path maintains stable voltage during battery transitions and protects sensitive robot electronics. Battery performs SOC calibration, keeping accurate runtime estimation after each swap and preventing shutdowns.
Modular & Scalable Battery Platforms
Inconsistent battery dimensions, limited installation space, and scalable capacity needs are same AMRs battery challenges for engineers. Parallel system handling involves issues like thermal imbalance, current drift, connector resistance variation, and unequal cable lengths. It lead to SOC mismatch or early aging in poorly designed systems. Professional lithium battery manufacturers address these issues by offering standardized modular platforms:
- One-size multi-capacity design. AMR lithium battery pack ranging from 20Ah to 150Ah battery packs share the same footprint, reducing tooling and engineering cost for enterprises.
- Parallel-ready architecture with master–slave BMS management. Adopt automatic balancing, and CAN ID coordination to extend runtime safely in mobile robot.
- Custom mechanical form factors. Thin, L-shaped, U-shaped, under-motor embedded design to fit the diverse configuration and tight space of autonomous mobile robots.
- Standardized fast-swap interfaces. Simplify maintenance and future product scalability.
High-Power & Fast-Charging Architecture
High-performance AMRs batteries demand both strong peak discharge and stable continuous current, which are the fundamental capabilities of high-C discharge capability, stable temperature control, and efficiency.Therefore, the battery manufacturer must guarantee.
- Low-Impedance current path and busbar design. It ensures symmetrical, equal-length, equal-resistance conduction routes, reducing I²R heating under high-power operation.
- High-C Discharge Platform. Mobile robots experience frequent high-power load changes during lifting, acceleration and turning, which determine the safe heavy-load operations. Low-decay, high-safety cell selection and dynamic current limiting handling by BMS.
- Intelligent Thermal Management for Fast Charging. Effective thermal management impacts safety, lifetime, and charging efficiency. Thermal-path modeling and simulation, cell-level and module-level temperature equalization are vital for fast-charging safety.
Case Study: CM Batteries 48V 55Ah Prismatic NMC Battery Pack for AMRs
An automatic mobile robotics manufacturer approached us with need for 48V high-energy-density battery pack designed for outdoor and all-weather autonomous systems. Their requirements are clear and uncompromising: a lightweight battery design to maintain AMR mobility, extended runtime for 24/7 warehouse operation, long cycle life for durability, and RS485 communication for seamless integration with their control system.
Customer Requirements
AMRs now shoulder the most demanding tasks in automated warehouses, and their batteries ultimately define their mobility, uptime, and overall reliability. Here are major challenges that our customer concern.
Is the battery light enough to support agile and efficient robot movement?
Can it provide the extended runtime required for continuous operation?
Does it offer the long cycle life needed to keep maintenance costs under control?
Is the communication interface—such as RS485—sufficiently reliable for real-time system integration?
And can the AMR battery maintain stable performance across wide temperature conditions and fluctuating load demands?
The Solution & Key Design Highlights

Introducing our 48V 55Ah Prismatic NMC Battery Pack for Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs).
- Wide-Temperature Battery Technology. Custom electrolyte formulation and enhanced SEI design enable charging from -20℃ to 55℃ and discharging down to -30℃, ensuring stability in cold warehouses and outdoor logistics.
- Lightweight and high energy density battery pack. Using NCM prismatic cells and optimized mechanical layout, battery pack offers total weight of 12.3 kg while delivering long runtime and reducing the load burden on AMRs.
- Long cycle life for lower operational costs. Our NMC battery pack is built for frequent AMR duty cycles with 2000 cycles at 80% DoD, helping fleet operators reduce replacement intervals and long-term maintenance costs.
- Smart battery management system(BMS) for system Integration. The integrated BMS supports RS485 communication, enabling real-time access to SOC, SOH, temperature, voltage, current, and alarm logs. This ensures stable connectivity with AMR controllers and fleet management systems.
What Is the Technology Trend of Autonomous Mobile Robot Lithium Battery?
AI is reshaping how AMRs are deployed and maintained—and it raises the bar for the battery systems. For lithium battery manufacturers, the future market requires no longer only the safe and stable energy supply, but to deliver AI-compatible, data-rich, and predictable battery platforms. And solid-state batteries have emerged as a breakthrough technology that is revolutionizing the battery industry.
AI Enhance AMR Battery Data Accuracy and Safety
- AI improves battery data accuracy and enhances safety. AI-driven algorithms analyze SOC, SOH, and RUL data, along with multi-point thermal sensing, to predict battery usage and ensure performance. Similar to Siemens’ Safe Velocity and Operations Copilot, which use AI to adjust vehicle spehanceeds and operations. This battery data analysis enables AMRs to maximize efficiency, minimize downtime, and reduce maintenance.
- AI-driven fault prediction and learning algorithms. Engineers can train effective fault prediction models based on limited data, thereby improving the BMS intelligence level and reducing unexpected downtime during robot operation.
IoT Drive AMR Battery Optimization
- Battery Management System (BMS) and Edge Computing. Edge computing enables BMS to process and analyze data at the edge of the battery system, without the need to upload all data to the cloud. This reduces bandwidth requirements, increases response speed, and enhancing the overall operational efficiency of AMRs and automated factories.
- 5G and TSN Networks Accelerate Data Transmission. 5G supports high-frequency, low-latency data exchanges, ensuring instant communication between batteries and robots, while TSN guarantees the real-time data transmission, suitable for industrial automation and reliable IoT systems. It offer more efficient battery management systems (BMS) that support predictive maintenance and dynamic charge/discharge management.
Solid-state Battery Technology for AMR
Solid-state batteries are lighter, safer, and more durable, representing the next-generation battery solution for higher energy density AMRs.
- Compact and Lightweight Size. Solid-state batteries eliminate the need for bulky safety protection equipment, enhancing the flexibility of mobile robots.
- Solid-state batteries deliver higher energy density than that of conventional lithium batteries(Sung et al., 2023). This feature allows autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to achieve a longer operational range within the same volume, making them more efficient for extended missions. .
- They provide high structural stability, superior safety, and extended lifespan. Solid-state batteries have a lifespan of 5–7 years and can withstand up to 20,000 bends while maintaining stable performance, reducing battery replacement frequency and costs (Institute of Metal Research, 2025).
Conclusion: Boost AMRs Performance with CM Batteries
AMR manufacturers face growing pressure to improve runtime, safety, and fleet efficiency. High-load missions, frequent charging, cold-start scenarios, and the data visibility are core bottleneck in AMR deployment.
To solve these challenges, the first layer is basic battery technology. Stable lithium chemistry, optimized thermal design, robust protection circuits and right communication protocols.
The next layer is advanced battery technologies. Intelligent BMS provide real-time SOC/SOH, thermal monitoring, fault logs, and health analytics. Cloud-ready communication protocols (CAN/CAN FD, RS485, BLE) enable seamless integration with AI scheduling systems.
CM Batteries offers custom lithium-ion battery packs for AMRs, featuring BMS algorithms, cloud-ready communication, wide-temperature battery technology, and lithium chemistries such as NCM and LiFePO4. We work with robotics engineering teams to design reliable AMR lithium battery that improve total cost of ownership. If you have any requests, please contact us.
FAQs About Lithium Battery for Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
LiFePO4 VS NMC Batteries:What are Their Performance for AMRs?
NMC batteries offer longer range, lighter weight, and greater power output, along with excellent low-temperature performance, ideal for AMRs requiring longer operating time and robust power output. LiFePO4 batteries offer superior safety, ultra-long lifespan, and economic efficiency. Their superior thermal stability and longer cycle life provide reliable protection for AMRs needing high-intensity continuous operation, and reduce the total cost of ownership.
Why Do AMRs Choose Lithium-ion Batteries Instead of Lead-acid Batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries have more merits compared with lead-acid batteries in AMRs, such as lightweight design, higher energy density, longer cycle life, no memory effect and faster charging, reducing replacement costs and enhancing overall efficiency.
What Is “Opportunity Charging” and Why Does It Matter for AMRs?
Opportunity charging refers to autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) automatically heading to a charger to recharge their batteries during idle time, instead of waiting for the batteries to fully discharge. It allows AMRs to maximize uptime by avoiding long offline charging sessions, reduces oversized battery packs needs and enables continuous operation.
How to Maintain and Extend the Lifespan of the AMR Lithium Battery?
Proper use and maintenance are crucial. Avoid extreme temperatures and charge during 0℃ and 45℃ ideal temperature. Set reasonable low-battery warning threshold(eg., 20%) to allow the robot to return to charging. Avoid prolonged storage at full charge and keep the battery level between 40% and 60% if the AMR needs to be idle for extended period.
How Does CM Batteries Ensure Safety and Reliability of Battery Packs During High-load AMR Operation?
CM Batteries takes priority of advanced safety and reliability.
Cell-level safety. We rigorously select top-tier cell suppliers and collaborate with partners to develop custom battery packs.
System-level safety. We develop intelligent battery management system (BMS) features monitoring, high-precision state estimation, intelligent thermal management, providing proactive safety protection.
Structural-level safety. Our battery pack employs industrial-grade structural design, offering shockproof and leak-proof features, ensuring safety in harsh conditions.










One thought