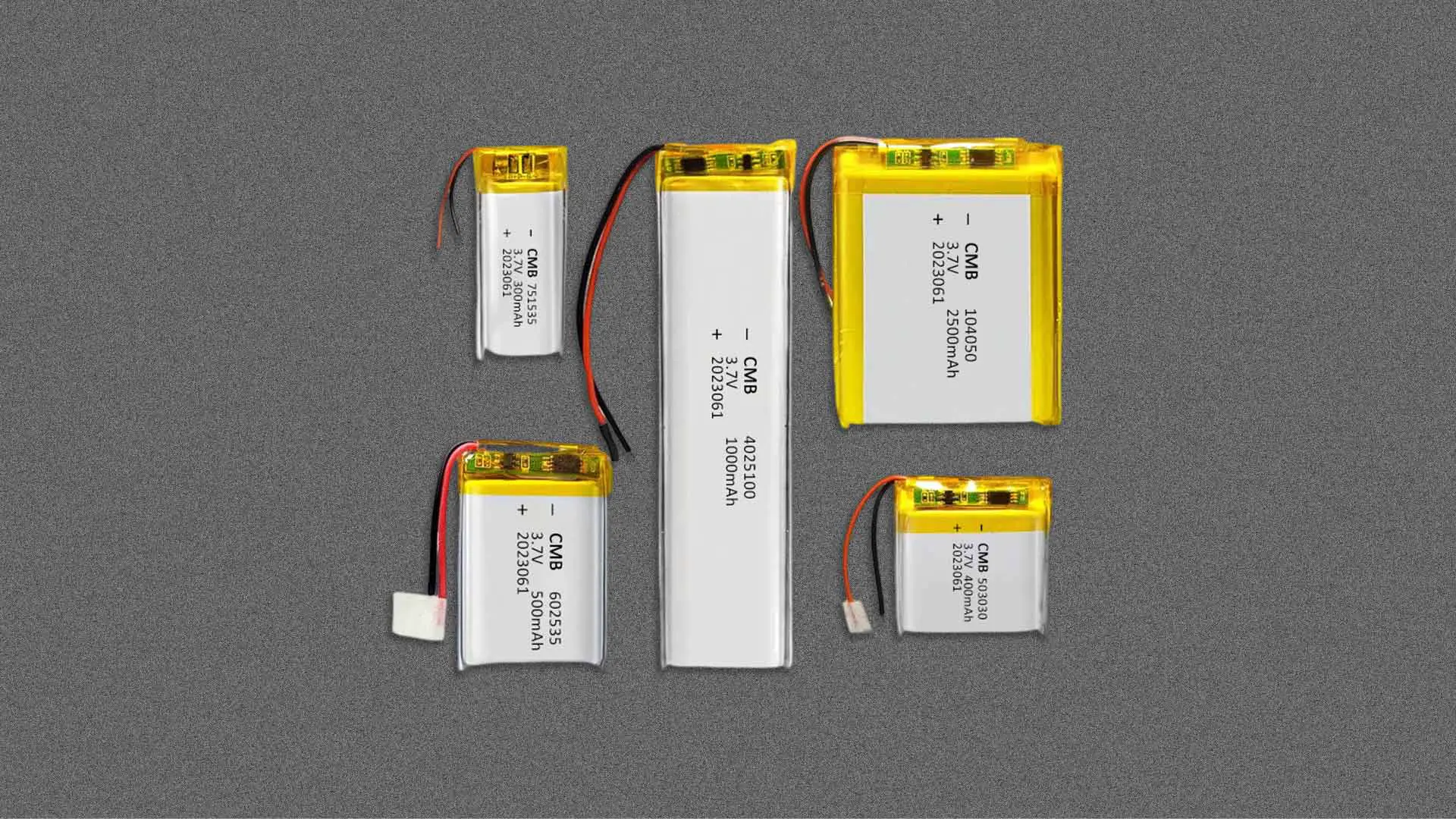
In the realm of rechargeable batteries, two popular options are Lithium Polymer (LiPo) and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries. We need clear results about LiPo vs LiFePO4 to select the right battery for our devices. They own their unique characteristics for different applications. This article will show the main differences between LiPo and LiFePO4 batteries, their pros & cons, and applications to determine which one is right for your needs.
LiPo Batteries VS LiFePO4 Batteries In Definition, Pros & Cons
Lithium Polymer (LiPo) Batteries Definition
The cathode and anode materials used in lithium-polymer batteries are the same as in liquid lithium-ion batteries, with cathode materials including lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganese oxide, ternary materials, and lithium iron phosphate, and the anode being graphite. The main difference lies in the electrolyte: liquid lithium-ion batteries use liquid electrolytes, while polymer lithium-ion batteries use solid polymer electrolytes.
As a result of replacing the liquid electrolyte with a solid electrolyte, compared with liquid lithium-ion batteries, lithium-ion polymer batteries have the advantages of thin, custom shapes. The battery shell is manufactured with aluminum-plastic composite films, which improve the capacity. Besides, lithium-ion polymer batteries are made of anode polymer materials. The mass-specific energy will be over 20% higher than the current, compared to liquid lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion polymer batteries have the characteristics of various shapes, thinness, and lightweight.

Lithium polymer battery pros and cons:
Advantages:
- Thin Dimension: Lithium polymer batteries can be designed with thin dimensions, compared to cylindrical or square lifepo4 batteries.
- Lightweight: The polymer electrolytes do not require a metal shell for protection, which makes them weigh 40% less than steel-cased lithium batteries of equivalent capacity and 20% less than aluminum-cased batteries.
- Custom Shapes: The battery pack manufacturers not only design the standard shapes but also produce custom shapes according to your needs.
- High Energy Density: Lithium polymer batteries offer higher energy density.
- High Discharge Rate: Lithium polymer batteries have higher discharge rates even with 50C and 70C discharge rates which are widely used for UVAs.
Cons:
- Shorter Cycles: After discharge cycles, the capacity of lithium polymer batteries degrades rapidly.
- Temperature Range Limit: They may not perform in wide temperatures for discharge & charge.
- Weak Charge Performance: Overcharging or over-discharging will damage the reversibility of internal chemicals in the battery without PCB.
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Batteries Definition
The lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery refers to a lithium-ion battery that uses lithium iron phosphate as the positive electrode material. The positive electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries mainly include lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganese oxide, lithium nickel oxide, ternary materials, lithium iron phosphate, etc. However, lithium cobalt oxide is currently used as the positive electrode material in the vast majority of lithium-ion batteries.

The nominal voltage of LiFePO4 batteries is 3.2V, the full charge voltage is 3.6V, and the cut-off discharge voltage is 2.0V. Due to differences in the quality and processes of positive and negative electrode materials and electrolyte materials from different manufacturers, there are some differences in performance. For example, the same standard battery size has a 10% to 20% capacity difference.
Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) power batteries exhibit a wide range of capacities, categorized into three distinct groups:
- Small Capacity: These batteries’ capacity ranges from 1800mAh to 6000mAh, which has larger discharge rates of 5C to 10C. They are widely used for power tools, robots, etc.
- Large Capacity: The capacity ranges are from 50Ah to 200Ah with less discharge rates from 1C to 2C.These batteries are ideal for high-power applications like electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and big agriculture robots.
This article “What is a lifepo4 battery” provides more insights into the benefits, drawbacks, and applications of LiFePO4 batteries, which can be helpful for those looking to gain a deeper understanding of lithium iron phosphate batteries.
The Features: LiPo VS LiFePO4 Batteries
Battery Structures
There are some differences in the battery structure between lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries and lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries. LiPo batteries use a polymer electrolyte and are encased in aluminum foil or a steel shell, providing a very high overall battery strength. On the other hand, LiFePO4 batteries utilize lithium iron phosphate as the positive electrode material and are encased in a liquid electrolyte. Relatively, LiPo batteries exhibit stronger resistance to impacts, whereas LiFePO4 batteries are known for their enhanced safety and stability.
Performance Variations
In terms of performance, lithium polymer batteries offer higher energy density and nominal voltage while being relatively lightweight. They also have a higher self-discharge rate and minimal energy loss over time. On the other hand, lithium iron phosphate batteries exhibit better stability and longevity in low-temperature environments. Overall, each type of battery has its performance advantages and disadvantages in various application scenarios.
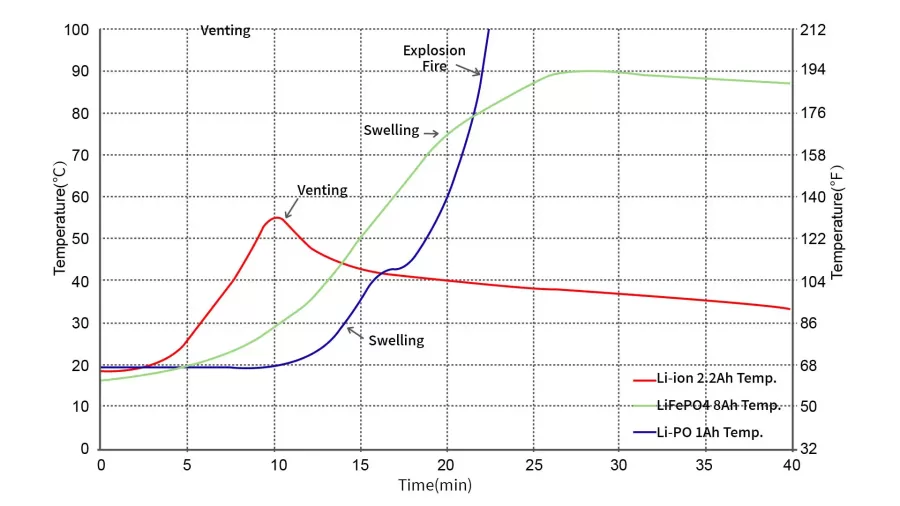
Safety
Due to the inherently high thermal stability of the electrolyte in li-polymer batteries, lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries exhibit higher safety levels under extreme conditions. On the other hand, lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries do not contain flammable or explosive materials inside the battery, thus minimizing serious safety hazards in high-temperature or extreme environments. Under typical daily usage conditions, both types of batteries offer assured safety levels.
Lipo Batteries VS LiFePO4 Batteries
| Feature | LiFePO4 Battery | LiPo Battery |
| Charge Frequency | Every 6-12 months | Monthly |
| Cycles | Up to 2000 cycles | Up to 500 cycles |
| Discharge Temperature | -20°C to 60°C | -20°C to 60°C |
| Ideal Operating Temperature | 0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F) | 0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F) |
| Storage Temperature | -20℃~25℃ | 0℃~25℃ |
Applications
Due to the higher energy density and lightweight of lithium polymer batteries, they are primarily used in some devices:
- IoT devices: LiPo batteries offer continuous operation for IoT sensors and trackers because of their lightweight and thin size.
- Medical Devices: LiPo batteries power a wide range of medical devices, from portable monitors to implantable devices, providing reliable and efficient operation.
- Industrial & Commercial Applications: LiFePO4 batteries power a diverse range of industrial and commercial equipment, including Marine, Golf Cart, and RV.
- Electric Surfboards: The higher discharge rate and long lifespan of LiFePO4 batteries make them ideal for electric surfboards.
- Robots: LiFePO4 batteries provide reliable power for robots because of their reliable safety
As a manufacturer of custom LiPo battery packs and LiFePO4 battery packs, CM Batteries should understand your specific requirements before designing a unique battery pack solution. Whether you prioritize compactness and high energy density (LiPo) or prioritize safety and longevity (LiFePO4), CM Batteries ensures optimal performance for your applications with the longest and most reliable custom battery packs.
In conclusion, the choice between LiPo and LiFePO4 batteries depends on a comprehensive evaluation of your device’s needs and operation environment. With CM Batteries’ expertise in custom battery solutions, you will get the battery pack with precision and reliability. CMB is a leading custom battery pack manufacturer. Contact us to explore tailored LiPo and LiFePO4 battery pack solutions.











One thought