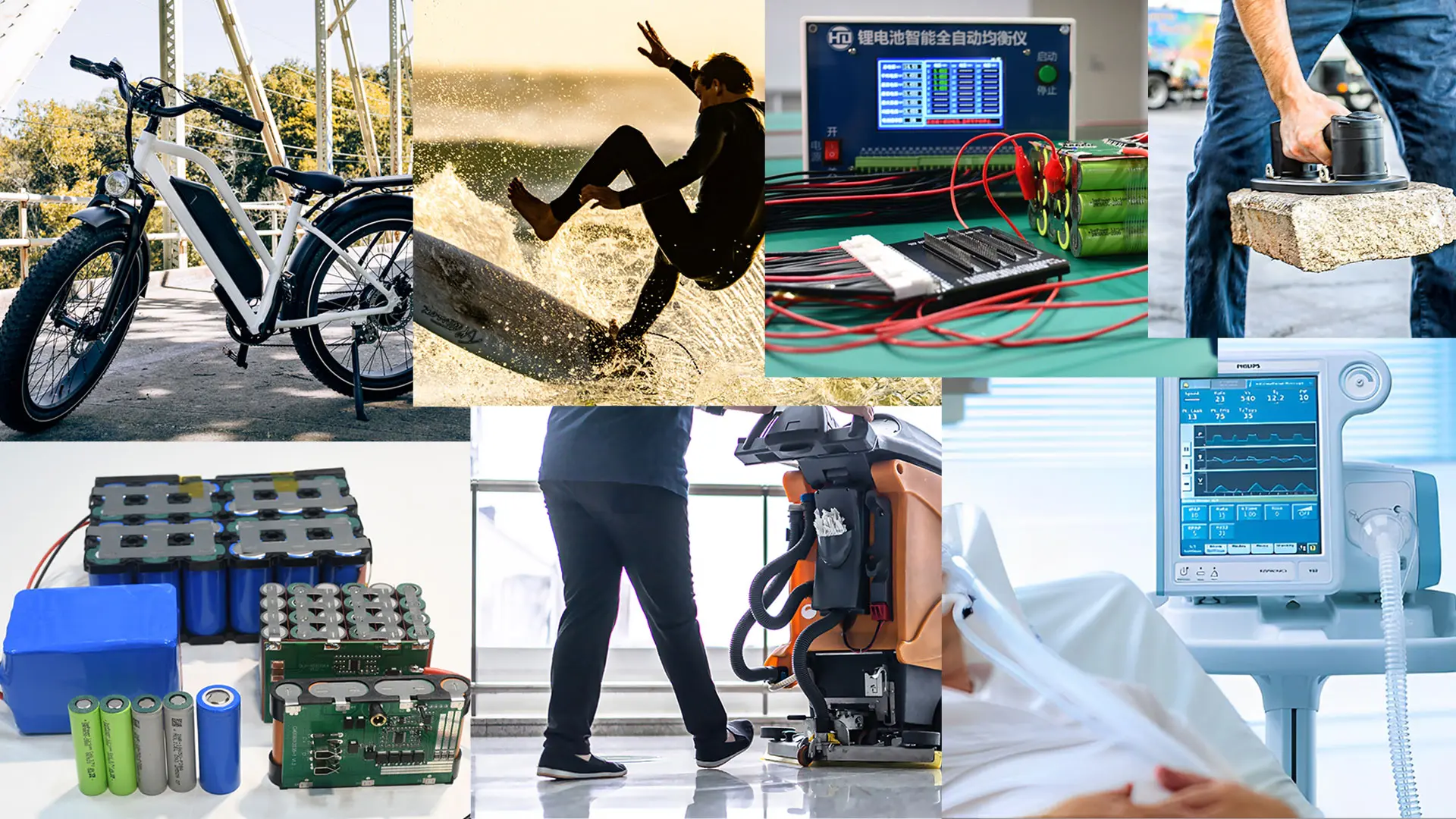
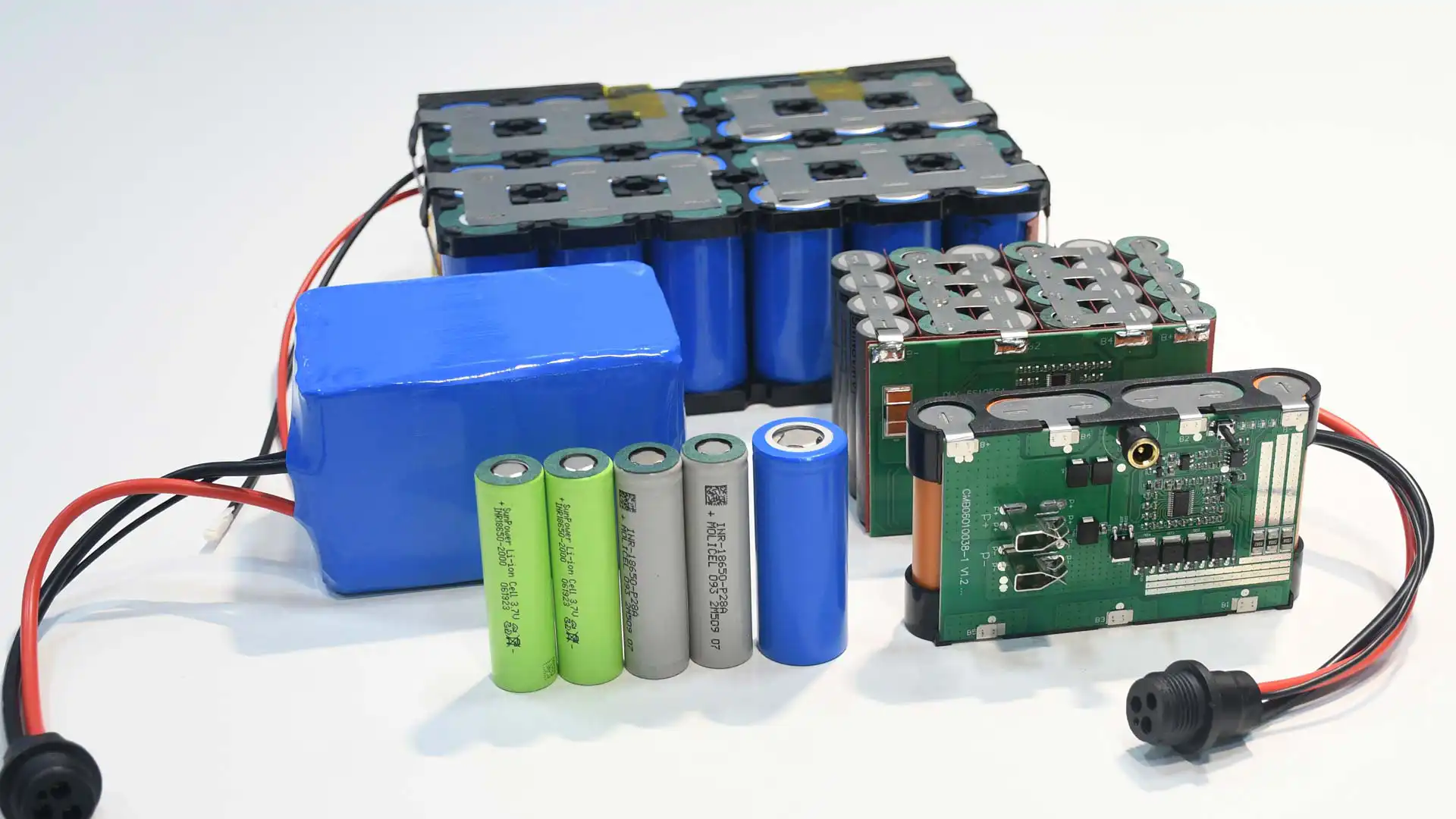
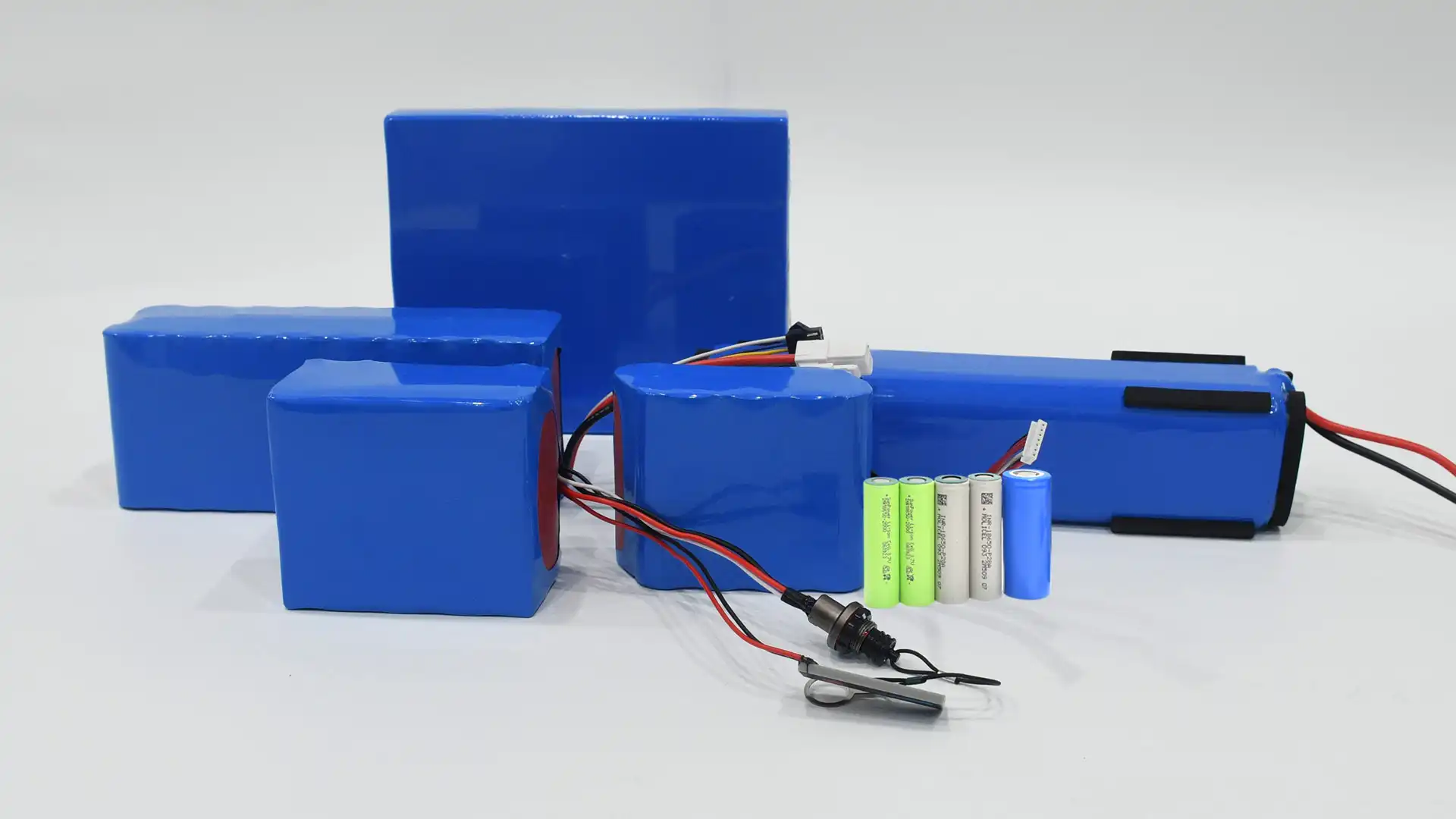
While the terms “battery cell,” “battery module,” and “battery pack” are often used interchangeably, the battery cell module pack refers to different stages of the battery’s construction. Battery cells are the basic electrochemical units. Modules are made up of multiple cells that work together to improve capacity and voltage. Packs are full assemblies that include modules, BMS, and other parts that are needed for a certain job. Understanding these distinctions is crucial, especially when discussing battery systems for larger applications such as electric vehicles or energy storage systems.
Basic Unit of A Battery Pack: Battery Cells
At the heart of every battery pack lies the humble battery cell. It functions as the fundamental energy storage unit where electrochemical reactions take place to store and release energy. The characteristics of battery cells—such as their shape, size, and chemistry—significantly influence their performance, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
- Cylindrical battery cells: They are labeled based on their dimensions, likely 18650, 21700, 26650, and 32700. They are known for their durability and ability to handle high power, making them ideal for use in laptop batteries, power tool batteries, ebike batteries, mobility device batteries, and robot batteries. Besides, cylindrical battery cells have some advantages such as high mechanical stability, thermal management, and low-cost production.
- Prismatic cells: They are known for their relatively good safety performance and more flexible dimensions than cylindrical batteries. They are useful for producing large-capacity batteries and are well-suited to the battery pack group. Because of their simple manufacturing method, prismatic batteries are ideal for large-scale production. Large prismatic batteries with individual cell energy over 1 Kwh are widely employed in a variety of applications. Furthermore, blade-type batteries have expedited the manufacturing process by eliminating the requirement for battery module assembly, which simplifies the battery group. The Common prismatic battery cells are classified into 3.2V 50Ah LiFePO4 battery cells, 3.2V 100Ah LiFePO4 battery cells, 3.2V 200Ah LiFePO4 battery cells, and 3.2V 280Ah LiFePO4 battery cells.
- Pouch cells: They are an excellent choice for applications where space efficiency and customization are critical. Their flexibility in design and form factor makes them ideal for portable and compact devices. Due to their thin profile and high energy density, they are commonly used in smartphones, tablets, laptops, and consumer electronic devices.
Each cell type has its unique features, such as capacity, voltage, and chemistry.
A Unit Assembled from Multiple Battery Cells: Battery Modules
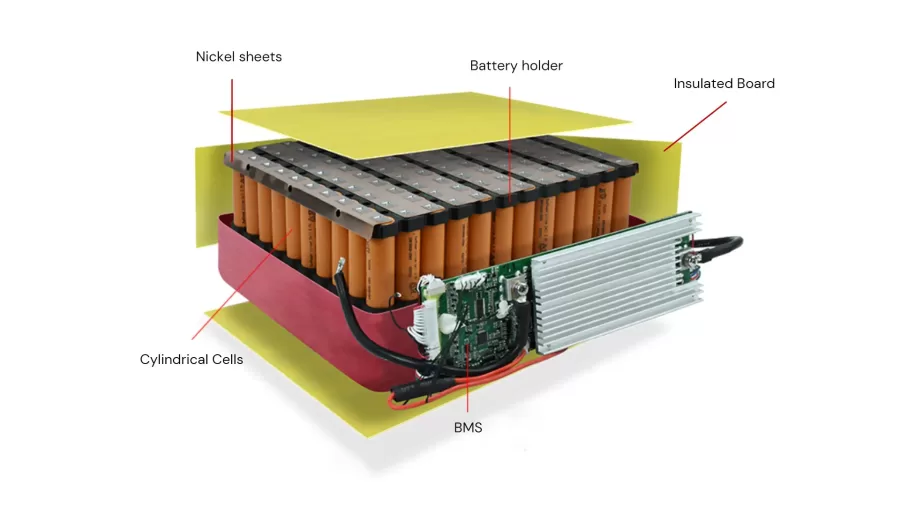
The Li-ion battery model integrates series-parallel connected cells, a structural framework, and a battery management system. Each module contains several critical components, including module control units, battery cells, conductive connectors, plastic frames, a cooling system, end plates, and fasteners that hold everything together.
The battery module is an essential component of the battery management system, acting as a link between individual cells and the entire battery pack. It is in charge of monitoring and regulating each cell’s performance, safety, and level of charge. A complete battery pack combines numerous modules, which are handled by one or more battery modules. This hierarchical structure enables the efficient control of large-scale battery systems, such as those used in electric vehicles or grid-scale energy storage.
The battery modules operate together with the overall Battery Management System (BMS) to improve the performance, safety, and longevity of the battery pack. It plays an important function.
- Thermal Runaway Prevention
- Pack-level Diagnostics
- Performance Optimization
- Lifespan Management
What Does A Battery Control Module Do?
The full name of BCM is Battery Control Module. Its role is like a “battery manager.” It helps the battery pack check its “health” and “charge level,” making sure each battery cell works properly without getting too hot, too cold, or overcharged. If a battery cell shows signs of “illness,” the manager will alert and stop the cell from working to prevent further damage. This protects the battery pack, extends its lifespan, and keeps the entire system safe and reliable.
The Complete Package: Battery Packs
What is a battery pack? A battery pack is an integrated assembly of many battery cells or modules that serve as a single, unified power source. Engineers typically interconnect battery cells or modules and place them inside protective enclosures to ensure safe and efficient operation. They design battery packs to maximize performance, capacity, and voltage output while aligning with the specific needs of the application. It’s a thoughtful system that maximizes performance, capacity, and voltage output for specified usage. A battery cell module pack is the complete assembly, generally having many modules and several critical components:
- Battery Cells or Modules
- Battery Management System
- Cooling System
- Electrical Interfaces
- Protective Enclosure
The pack production lines have to fulfill two functions: assembly and package. Battery pack manufacturers typically use semi-automatic assembly lines to carry out essential processes such as soldering, welding, insulation, testing of semi-finished packs, and final packaging. For example, manufacturers connect two or more battery modules in series or parallel and arrange them into a specific configuration based on customer requirements. This final structure is called a battery pack. You can find some battery packs addressed by their voltage.
- 11.1-volt lithium battery pack
- 24-volt lithium battery pack
- 36-volt lithium battery pack
- 48-volt lithium battery pack
And increasing the number of cells in the battery pack arranged in parallel is increasing the capacity. Check out this article on 12V lithium batteries in series and parallel.
Battery Pack Design Factors
Numerous critical factors will affect the battery cell module pack design. Let’s explore more.
- Cell Selection: Determining the appropriate type and size of cells based on performance requirements.
- Thermal Management: Installing cooling systems to avoid overheating.
- Safety Features: Include safeguards against overcharging, short-circuiting, and other hazards.
- Electrical Connections: Using low-resistance connections to maximize efficiency.
- Enclosure Design: Creating a strong, safe enclosure that also enables effective heat dissipation.
Battery Cell vs Battery Module vs Battery Pack: Key Differences
A battery cell is a battery’s basic unit, whereas a battery module is a collection of battery cells. A pack, on the other hand, consists of one or more modules as well as any other components required for operation, such as enclosure, connectors, and control circuitry.
The following comparison chart demonstrates this in greater detail:
| Aspect | Battery Cell | Battery Module | Battery Pack |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Smallest electrochemical unit | Assembly of cells with basic controls | Complete system with modules, BMS, safety systems |
| Voltage Range | 3.2V – 3.7V | 12V – 48V | 48V – 800V+ |
| Capacity | 100mAh – 5000mAh | 0.5 kWh – 5 kWh | 1 kWh – 100+ kWh |
| Management System | Minimal or none | Module-level BMS | Full BMS: SoC, SoH, communication, safety |
| Thermal Management | Passive | Basic (e.g., heat spreaders) | Advanced (liquid, active air cooling) |
| Customization | Limited | Moderate | High (design, capacity, voltage, form factor) |
| Applications | Consumer electronics, medical | Automotive, energy storage | EVs, energy storage, industrial devices |
To ensure the reliability and safety of the battery cell module pack, each prototype battery pack undergoes rigorous testing, such as performance tests under various conditions, safety tests (overcharge, short-circuit, crush tests, etc.), life and cycle tests, and environmental tests (extreme temperatures, humidity, vibration, with selective focus on specific safety tests based on the functionality of the battery cell module pack.
The hierarchical structure of lithium-ion battery systems, from individual cells to modular designs and whole battery packs, exemplifies the complexity and versatility of battery technology. This layered design not only enhances the performance and durability of battery systems but also allows lithium-ion batteries to power a wide range of applications — from small portable devices to large-scale energy storage systems. Professional battery solution providers have become increasingly crucial. With its extensive experience in the field of lithium-ion batteries, CM Batteries provides custom battery pack solutions to match the individual needs of its customers.