It is snowing in the winter. People will choose the sport of skiing. The demand for electric skis is increasing. Electric ski manufacturers are looking for low-temperature resistance of lipo batteries. There are many applications such as electric skis, GPS trackers, seawater systems, car sensors, and aerospace industries that need the lipo battery to work in cold weather.
The performance of lithium polymer batteries will be affected by the low temperature. However, today’s technology can help you overcome this problem, so we’re going to take a deeper look at how cold temperatures affect LiPo batteries and how you can keep your LiPo batteries safe and reliable in colder temperatures.
What Damage will LiPo Battery Low Temperature Cause?
You must have noticed that during the winter months, our mobile phones consume power particularly fast. Cold weather can indeed affect the performance of LiPo batteries. As shown in Figure 1, a lower environmental temperature when our LiPo batteries are in use will result in the following:
Reduced Capacity
The primary reason for lower capacity at cold temperatures is the decreased mobility of lithium ions inside the electrolyte. Lithium ions are essential in the chemical reactions that create energy in LiPo batteries. As temperatures fall, the viscosity of the electrolyte rises, making it more difficult for lithium ions to flow between the electrodes. This reduced mobility reduces the battery’s ability to store and release electrical energy, resulting in a decrease in capacity.
Voltage Decreases
Another factor leading to voltage drops is the higher internal resistance of LiPo batteries in cold weather. Internal resistance is the intrinsic barrier to the flow of electrical current within the battery. As temperatures drop, the resistance of the battery’s components, such as the electrolyte and electrodes, rises. This increased resistance impedes the smooth passage of current, resulting in a perceptible voltage drop, especially when under load.
Increased Internal Stresses
Cold temperatures might cause internal strains inside the LiPo battery construction. Temperature variations can induce material contraction and expansion, putting mechanical stress on the electrodes and electrolytes. These forces can cause microcracks and deformations in the internal structure of the battery, jeopardizing its integrity and perhaps harming long-term performance.
Risk of Cell Damage
In extremely cold temperatures, the electrolyte in LiPo batteries can freeze, causing cell damage. The freezing of the electrolyte disturbs the ion transport pathway, preventing electrochemical processes from taking place. Furthermore, the frozen electrolyte’s expansion can cause physical damage to the cell separators and membranes, resulting in leakage and possible fire concerns.
Voltage Fluctuations
Rapid temperature changes can cause voltage swings in LiPo batteries. These variations are caused by the varied conductivity and reactivity of the battery materials at various temperatures. Sudden temperature changes can upset the electrochemical reaction balance, generating voltage spikes or decreases. These oscillations can disrupt the battery’s functionality and pose possible safety issues.
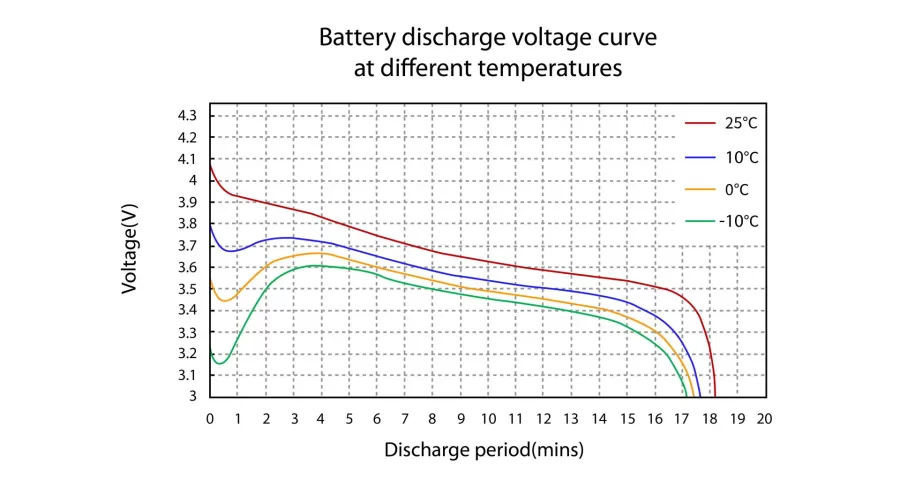
Fortunately, technological advances have facilitated the development of low temperature resistant lithium polymer batteries that address the pain points associated with cold weather.
For example, doping the electrode material with specific elements can increase its conductivity and ion diffusion rate, allowing for efficient charge transfer even in cold environments. There are also some low-temperature lithium polymer batteries that employ internal heating mechanisms. These mechanisms, such as self-heating elements or resistive heaters, generate heat within the cell to raise its temperature to a range more suitable for efficient operation. This internal heating helps maintain consistent performance and prevents voltage drop, especially when subjected to high current or low temperature environments. These technical measures can generally withstand low temperatures of -40°C or even lower.
Charging and Discharging Lithium Polymer Battery Temperature Range in Different Seasons
Lithium-polymer battery operating temperatures range from 0 to 35°C are optimal, with optimal charging and discharging temperatures between 15°C and 35°C. However, it’s essential to consider how seasonal temperature changes affect these batteries.
At low temperatures, the activity of lithium ions decreases, resulting in lower discharge capacity and shorter overall use time. But while these effects are temporary, they affect the capacity of the battery. Fortunately, once the temperature rises, the battery’s performance recovers, but this must be if it is used for a short period of time in a cold environment. The permanent damage to the battery capacity can be caused by prolonged use at low temperatures. Find out more.
Charging and Discharging LiPo Batteries in High Temperatures
It is recommended to follow certain guidelines for charging and discharging lithium polymer batteries:
Charging
- Charging should be done at temperatures ranging from 5 to 45°C.
- The charging voltage should not be more than 4.22V, and the charging temperature should not be higher than 45°C.
- Charge the battery at room temperature (35°C) and use it within 48 hours of charging. When not in use, the battery should be depleted to the storage voltage (3.8-3.9V) as soon as possible.
- If the battery has recently been depleted or exposed to extreme temperatures, the surface temperature must be less than 40°C before charging.
- Only the manufacturer’s recommended charger should be used to charge the battery, and any other equipment that delivers high current (1.5C) to the battery should be avoided.
Discharging
- Discharge must take place between the temperatures of 0 and 45°C.
- The discharge current must not exceed the maximum current indicated by the battery.
- The discharge’s lower warning voltage should not fall below 3.6V, and the rebound voltage shall not fall below 3.65V. Ensure that the battery surface temperature does not exceed 70°C after a high-current discharge.
- Avoid exposing the battery to sunlight before or after discharge, and before discharging, the battery surface temperature should not exceed 45°C.
Charging and Discharging LiPo Batteries in Low Temperature
The following guidelines are recommended for charging and discharging lithium polymer batteries:
Charging
- Charge the battery at room temperature (above 5°C, ideally 20°C). Charging should be avoided in high-temperature situations (40°C).
- Allow the battery to come to room temperature if it has been exposed to the outdoors.
- Avoid using equipment that provides high current (1.5C) to the battery and only use the manufacturer’s approved charger.
Discharging
- After discharging, thoroughly insulate the battery to keep it above 10°C (20°C is ideal). This can be accomplished with the use of a thermos cup, thermos box, or other comparable insulating methods.
- After loading the battery into the aircraft, use an app to verify the remaining battery power and voltage information.
- Avoid executing significant maneuvers if the battery temperature is less than 20°C.
- It is crucial to remember that the battery’s service life decreases dramatically in low-temperature situations as compared to room temperature (about 20°C). As a result, if you receive a low battery warning, you should immediately recharge the battery.
It is essential to be aware of the recommended temperature range for these processes to maintain the battery’s performance and safety.

Can LiPo Batteries be Stored in Cold Weather?
LiPo batteries can be stored in cold weather, but it’s important to take precautions to ensure their safety and longevity. When storing LiPo batteries in cold weather, the following guidelines should be followed:
- Bring the battery to room temperature: LiPo battery storage temperature range is 15°C to 30°C. Make sure the battery is at room temperature before storing it. If the battery has been exposed to cold temperatures, allow it to gradually warm up to room temperature (without using any heat source) before storing. This prevents heat shock and possibly battery damage.
- Insulate the battery during storage: If the battery is to be stored in a cold area without a temperature-controlled storage facility, it must be appropriately insulated. To protect the battery from freezing conditions, use insulating materials such as foam or a thermal bag. This contributes to keeping the battery’s temperature within a safe range.
- Regularly monitor the battery: During storage, check the battery’s voltage to verify it remains within the specified storage range. Consider recharging the battery if the voltage decreases sufficiently to avoid over-discharge.
Although there are many guidelines, I would recommend avoiding exposing fat batteries to extreme cold weather conditions for extended periods of time. Extreme cold temperatures can still affect battery performance.
Understanding the effect of cold weather on lithium polymer battery performance is critical for optimal usage and lifespan. You can bypass the constraints imposed by cold weather by using low-temperature-resistant LiPo batteries. Furthermore, according to the charging, discharging, and storage recommendations will result in increased battery life and safety. Don’t let the weather ruin your experience with LiPo batteries; take these steps to get their benefits all year.


