In today’s world of portable power, lithium and alkaline batteries dominate the market—but they serve very different purposes. Understanding the key differences between these battery types is essential for optimizing performance, cost-efficiency, and device compatibility. Let us explore about the definitions, critical differences in performance, lifespan, and cost.
Lithium VS Alkaline Batteries: Definitions
Before diving into comparisons, let’s establish what makes each battery type unique. Knowing these fundamental differences will help you make smarter power choices for your devices.

What is Lithium-ion Battery?
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable power sources that operate through the movement of lithium ions between positive and negative electrodes during charge/discharge cycles. This advanced technology offers superior energy density compared to traditional battery types.They are classified into cylindrical lithium-ion battery (such as 18650, 21700,26650), prismatic lithium-ion battery, and soft-pack battery according to their shapes. However, lithium-ion batteries can also be divided into ternary lithium batteries, LiFePO4 batteries, lithium manganese oxide batteries, and Lipo batteries by the materials.
The article “Understanding Different Lithium Battery Types” explains common lithium batteries like LFP and LTO. It compares their performance, design, and uses to show the differences, which is helpful for readers to gain a deep understanding of lithium batteries.
What is Alkaline Battery?
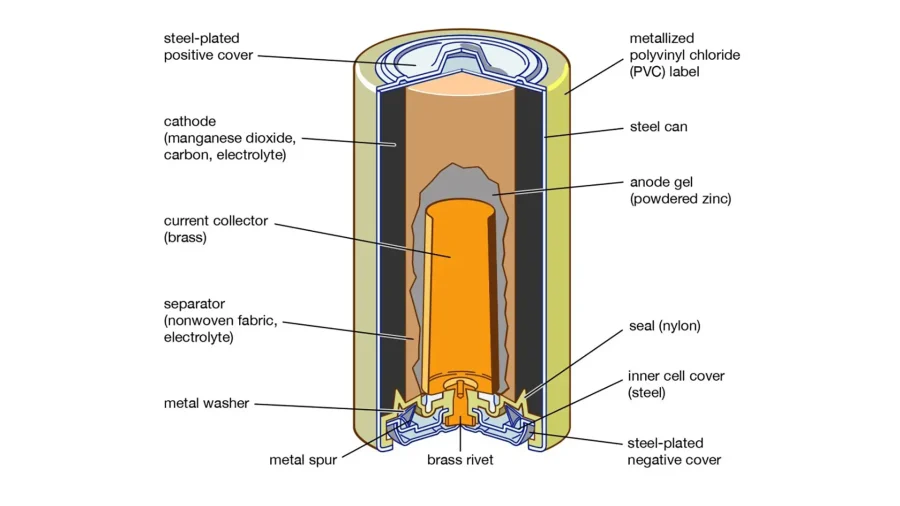
Alkaline batteries are a common type of primary battery. They are composed of zinc as the positive electrode material and manganese dioxide as the negative electrode material. When two metals contact, they generate static charge and create a closed circuit in the medium, producing current. Alkaline batteries are cheap and can be used as household batteries to replace carbon-zinc and zinc-chloride batteries. They typically have a voltage of 1.5V and maintain a relatively low internal resistance. Cylindrical alkaline batteries are common and have various sizes, such as AA, AAA.
What is the Difference between Lithium VS Alkaline Battery?
As an engineer purchasing batteries for a project, learning the key differences between lithium-ion and alkaline batteries helps choose wisely. These factors can affect the reliability and long-term cost of equipment operation.
Lithium VS Alkaline Batteries Structure
Alkaline batteries are primary batteries. AA alkaline batteries like Nanfu and Duracell use zinc powder as the negative electrode and manganese dioxide as the positive electrode. They also contain potassium hydroxide as the electrolyte, with a sealed casing to prevent leakage. Although they cannot support repeated charges, this simple structure makes them inexpensive and suitable for low-power devices.
In contrast,lithium-ion batteries have a more complex structure. Their anode material is LiFePO₄, while the cathode utilizes graphite. And their electrolyte consists of flammable organic solvents and lithium salts. Lithium-ion battery stores much energy by moving lithium ions between electrodes. During charging, lithium ions flow from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte, while electrons move outward. Discharging reverses this process. To prevent overcharging or short-circuiting, lithium batteries must have a protection mode. CMB’s battery management system(BMS) solves overcharging risks that worry engineers. It tracks battery voltage and temperature to trigger safety measures, while letting teams check battery health remotely. Custom design adds built-in heating to prevent moisture issues and smart wake-up modes. Real tests in warehouse robots show 90% less wasted power and fewer breakdowns.
Alkaline VS Lithium Batteries Energy Density
Lithium batteries offer higher energy density, almost 150-250 Wh/kg in a compact size. Alkaline batteries have a smaller energy density of 80-100 Wh/kg. When it comes to high-performance applications, like emergency equipment, the advantages of lithium batteries become prominent. High-energy-density LiFePO4 battery reduces the volume of the AED battery compartment by 40%, improving the portability and battery life of emergency equipment.
Compared with the single-use limit of alkaline batteries, the 3,000-cycle deep cycle life of LiFePO4 batteries (DOD 50%) can extend the battery life cycle by more than 8 times, adapting to frequent charging and discharging needs. Clinically proven, after standing in a 5°C medical refrigerated environment for 12 months, LiFePO4 battery maintains 95% of its power, while the alkaline battery is reduced to 65%.
Lithium VS Alkaline Batteries Cost
According to different battery capabilities, types, brands, the cost of lithium-ion battery and alkaline battery is different. The single-cell cost of lithium-ion batteries is indeed 6 times that of alkaline batteries. Taking a common model as an example, a 3.7V Samsung 2500mAh 18650 Li-ion battery cell costs $3, compared to a 1.5V NANFU AA Battery costs $0.5. However, if we compare energy cost performance, the gap between lithium-ion batteries and alkaline batteries has narrowed. From the energy density aspect, if calculated by unit energy cost (Wh/dollar), lithium-ion batteries (3.7V×2.5Ah=9.25Wh) are about 3.08Wh/dollar, while alkaline batteries (1.5V×2Ah=3Wh) are only 6Wh/dollar, and the cost gap has narrowed to 2 times.
Lithium Battery VS Alkaline Battery Self-Discharge Rate
Alkaline batteries have a very low self-discharge rate, typically less than 1% per year. This makes them ideal for low-drain devices and long-term storage. They can sit idle for years and still retain most of their charge. Alkaline batteries are more appropriate for remote controls or emergency flashlights, which require long periods of low-power operation.
Lithium-ion batteries have a higher self-discharge rate of about 2-5% per month. Over 10 years, even when not in use, they can lose up to 10% of their charge, which means they need to be recharged regularly. Lithium-ion batteries are better suited for mobile phones, laptops, and power tools, which require frequent charging and higher power output.
Lithium VS Alkaline Batteries Temperature Range
Lithium batteries maintain operation within the range of -20℃ to 60℃, but their performance drops at low temperatures. At -20℃, lithium batteries’ capacity is reduced to 65% of the nominal value.
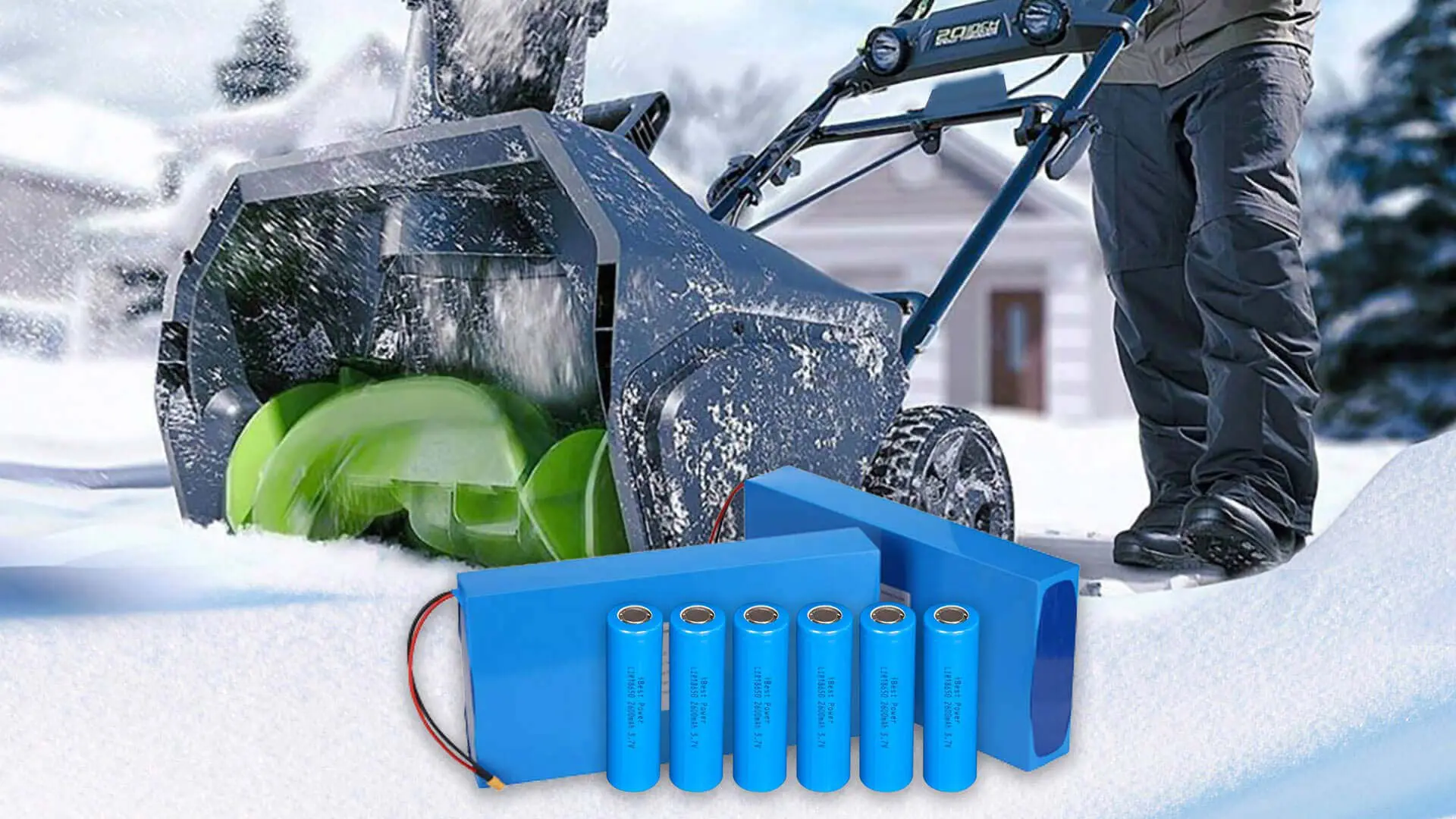
Alkaline batteries have more prominent low-temperature shortcomings, losing power supply capacity at -20℃. Taking outdoor cameras as an example, the capacity of ordinary lithium batteries in a -15℃ environment decays by about 35%, and alkaline batteries fail, causing frequent power outages in the equipment. Compared to ordinary lithium batteries, CM Batteries’ custom lithium-ion batteries operate in a wide temperature range of -40˚C to 85˚C, operating stably and cost-effectively in the long term.
Lithium-ion Battery VS Alkaline Ecological Impact
Rechargeable Li-ion batteries have over 500 times the cycle life compared with disposable alkaline batteries, which is conducive to resource recycling.
Alkaline batteries are prone to leakage, releasing corrosive substances and polluting soil and water, whereas lithium-ion batteries are less likely to leak due to the BMS for material safety.
For recycling value, lithium-ion batteries have a high recycling value, containing 90% recyclable metals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. However, alkaline battery materials have low value, and people discard them at will and causing pollution.
| Feature | Lithium-ion Battery | Alkaline Battery |
| Working Principle | Li-ion shuttling (reversible reaction) | Zn/MnO₂ irreversible redox reaction |
| Energy Density | High (150-250 Wh/kg) | Low (80-100 Wh/kg) |
| Cycle Life | 500-2,000 cycles | Single-use |
| Low Temperature performance | 65% capacity at -20℃ | Lose power supply at -20℃ |
| Cost | $3; High per unit; long-term | $0.5; Lower per unit; disposable |
| Applications | Ebike, robot, drone, drill, efoil, wearable devices | Remote control, alarm clock, mouse, electronic toys |
| Self-discharge | 2-5% per month | 1% per year |
| Eco-impact | Eco-friendly; High recycling value | Low recycling value; Improper disposal leads to pollution. |
Lithium VS Alkaline Batteries: Which is Better?
In the lithium vs alkaline battery race, the choice depends on your specific application needs. Alkaline batteries have low energy density and are suitable for short-term, low-budget applications, such as remote controls, electronic clocks, doorbells, digital cameras, and calculators. In contrast, lithium-ion batteries feature high energy density and are acceptable for long-term applications. Lithium batteries store twice as much energy as alkaline batteries, keeping power tools running longer. They recharge over 500 times, reducing long-term maintenance costs by 60%. At -20℃ conditions, alkaline batteries fail while lithium keeps the outdoor camera running.
What’s more, 90% of lithium-ion battery materials can be recycled, while only 5% of alkaline battery materials can be recycled. Smart safety systems in lithium batteries prevent the leakage and overcharging that are common in alkaline batteries. In addition, lithium batteries have BMS systems to monitor health and predict maintenance needs, dodging costly factory shutdowns from sudden power outages. For the EU’s new battery law, the recycling system of lithium batteries not only avoids penalties but also helps companies obtain green certification and enhance competitiveness.
CM Batteries is committed to manufacturing custom lithium-ion battery packs with compact size, custom design, and advanced BMS. Our wide temperature lithium battery packs can maintain 90% capacity at -40℃. If you have any custom requirements for the application, please contact us.