Battery Isolators play a pivotal role in power management systems, especially in RVs, marine vessels, and industrial devices with multiple batteries. It isolates different battery systems, optimizes charging and discharging efficiency, extends battery life, and safeguards critical power. This article explores types of battery isolators, their pros and cons, and their applications in dual-battery systems.
What’s a battery isolator?
A battery isolator is an electronic device to diverts electrical current, ensuring current flows in one direction. It separates the battery from the load, prevents batteries’ mutual interference, and improves battery life and safety. Battery isolators are used in various vehicles such as cars, ships, and trucks.
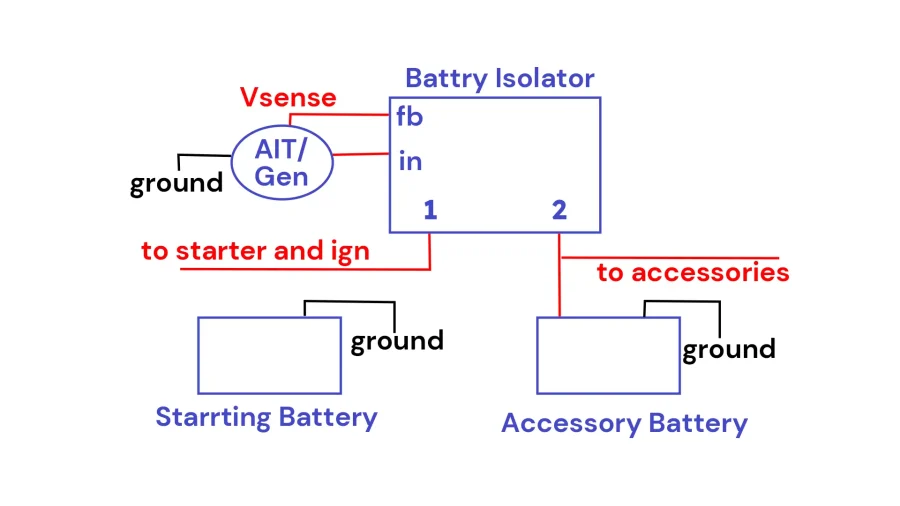
How does a battery isolator work?
A battery isolator protects your starter battery from being drained by the auxiliary battery. It disconnects the battery when the engine is turned off, saving you from struggling with a starter battery.
What is the function of a battery isolator?
Optimized charging, isolated discharge, emergency assist, and battery protection are the key functions of battery isolators. Grasping them to unleash the battery isolator’s potential.
1. Efficient Charging Management: Connect the starter and auxiliary battery in parallel to charge multiple batteries together. After charging the starter battery, charge the auxiliary battery subsequently.
2. Discharge Isolation: The Starter and auxiliary battery are isolated when the engine is turned off. Avoid exhaustion of the starter battery due to excessive discharge of the auxiliary battery.
3. Emergency Assist Start: Use the emergency auxiliary switch to connect the starter in parallel with the auxiliary battery. Utilize auxiliary battery power to start the vehicle.
4. Battery Protection: Battery isolators have constant voltage and current protection. It protects batteries from overcharging and extends battery life.
5. Reduce Voltage Drop: Relay-based battery isolators have no voltage drop. Compared to diode-based isolators, they minimize energy loss and enhance battery efficiency.
What are the types of battery isolators?
Common battery isolators disconnect have 5 types: disconnect switch battery isolator, diode-based battery isolator, relay-based battery isolators, Solid-State (MOSFET) battery isolator, and charger battery isolator. They have different operational methods for their merits.
Manual Isolator
Manually operate the knob of the battery isolator to control the contact of the internal copper sheet and stud, achieving the on and off of the circuit. This isolator shines for its simple structure, low cost, but manual control is easy to forget to operate.

Diode Battery Isolators
A diode battery isolator uses the unidirectional conductivity of the diode. The diode turns on when the output voltage is higher than the battery voltage, charging the starter and auxiliary batteries in parallel. It features high reliability but has a voltage drop of 0.7-0.9V, causing energy loss.
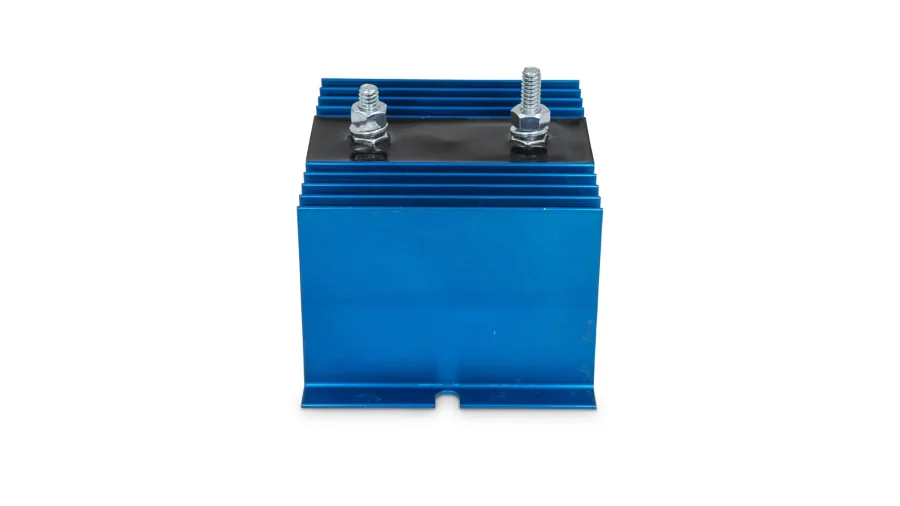

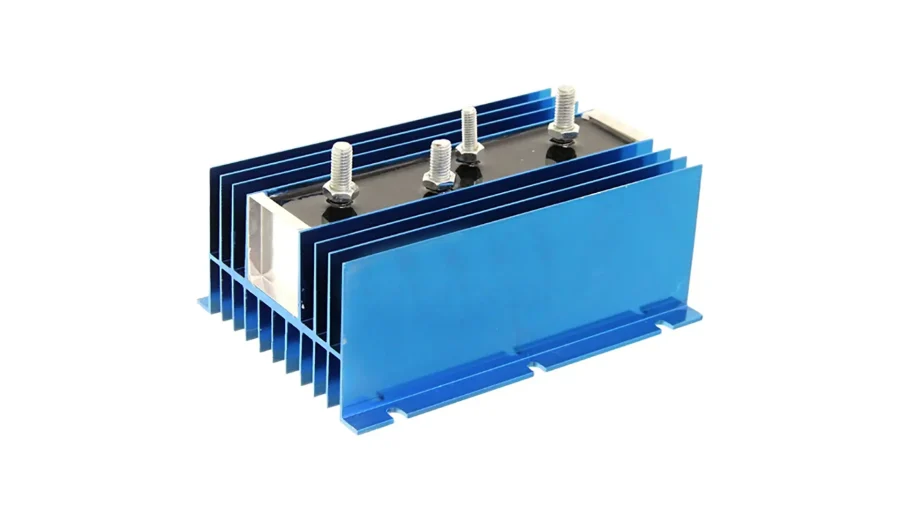
Relay Battery Isolators
Relay battery isolators monitor voltage and trigger switching at a set threshold to isolate the auxiliary battery. This isolator brings no voltage drop, and its wiring is simpler but more expensive.
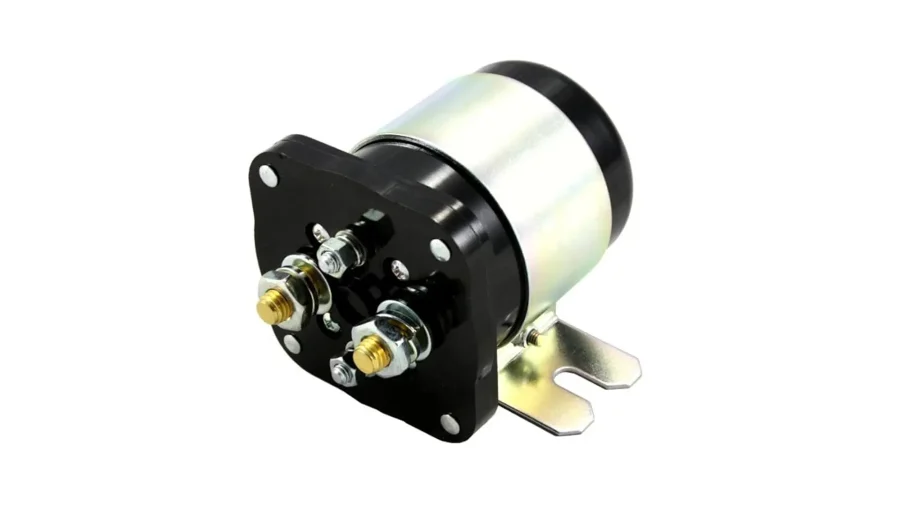

MOSFET Battery Isolators
This isolator takes mosfet as a current device, and offers MSU to achieve overcurrent and overvoltage protection. It has low heat generation and sound protection methods, but high cost.
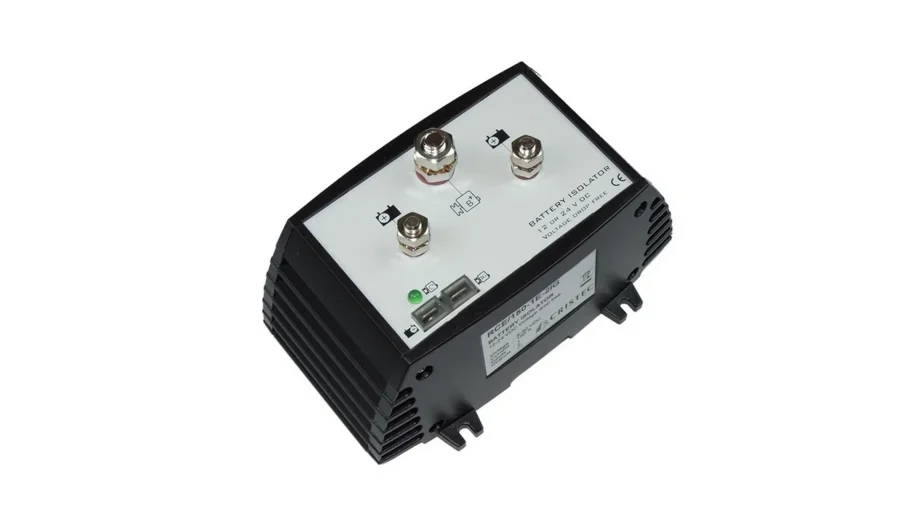

DC-DC Charge Isolator
This isolator performs a separator function, converting DC input to DC output. Starter and auxiliary battery power circuits are isolated when turned off. It stably charges for lithium battery with a low output voltage. But its current-limited output is not suitable for fast charging.

Benefits of Using a Battery Isolator
Installing a battery isolator possesses lots of merits. It protects the starter battery, improves charging efficiency, and enhances the safety of the battery system.
- Preserves starting power. It ensures the starter battery is in a sound state and free from the effects of drained auxiliary batteries.
- Support auxiliary battery charging. Battery isolators allow auxiliary batteries to power accessories without damaging the starter battery.
- Improve charging efficiency. Charging dual batteries in parallel. Isolation of auxiliary batteries during discharge ensures worry-free starting power.
- Enhance the safety of the battery system. Battery isolators block batteries. Abnormal consumption and the spread of circuit faults.
- Adaptability to various battery types. Battery isolators manage different batteries, such as lead-acid batteries, lithium batteries.
- Easy to install and use: The installation of the battery isolator is simple and doesn’t require complex modification of the original circuit. Some isolators have automatic control functions.
- Reliability for off-grid use. Battery isolators ensure backup power even if the starter battery is exhausted. They are ideal for RVs, boats, and trucks.
Disadvantages of Using a Battery Isolator
Battery isolators have multiple problems that decrease power performance and efficiency. Settle these issues to optimize the battery system.
- Voltage drop issue. When turn on diode battery isolator, the battery’s actual voltage decreases during charging and discharging.
- Capacity limitation: The capacity of the auxiliary battery must not exceed that of the starter battery. This limits power expansion.
- Size limitation: Diode battery isolators require the auxiliary battery to be smaller than the starter battery; otherwise affects the operation of the isolator.
- Reduces charging efficiency. A diode battery isolator affects the battery’s full charge and discharge stability.
- High cost: Relay battery isolators are more expensive than diode isolators due to their more complex structure.
- Reliability issues: Relay-based isolator faces contact wear and poor contact issues, requiring strict inspection.
- Electromagnetic interference risk: Relay-based battery disrupts other electronics, like audio and navigation systems.
- Weak environmental adaptability: High temperatures, humidity, and vibrations fail relay-based isolator contacts, reducing their lifespan.
When do you need a Battery Isolator?
Battery isolators are crucial in these situations:
1. When the main battery’s starting power needs to be protected
When the secondary battery powers in-vehicle equipment (like a refrigerator or lights), the isolator disconnects the main and secondary batteries after the car stops. This prevents the secondary battery from draining the main battery and ensures the vehicle can start.
2. When charging needs to be managed intelligently.
While driving, the isolator prioritizes charging the main battery. Once the main battery reaches a voltage of 13.3V-13.5V (about 80% charged), the isolator connects the secondary battery to charge. This helps avoid generator overload and ensures the main battery is fully charged first.
3. When there is a special battery system
If the secondary battery is a starter type, like a lead-acid battery, the isolator protects it from high current during engine start. If the secondary battery has a different voltage than the main battery (like in a 24V system) or mismatched chemistry (like Li-ion with lead-acid), the isolator avoids direct charging. This prevents generator overload and the risks of a direct connection.
4. When emergency starting support is needed
The isolator has a manual parallel function. This allows the vehicle to start using the secondary battery if the main battery loses power.
Do you need a battery isolator for a dual battery system?
YES, we strongly recommend that you:
- Adding electrical devices for vehicles requires installing a battery isolator. If not used, the discharge of the auxiliary battery causes the starter battery to run out of power, affecting the vehicle’s operation.
- Use different types of batteries. Isolators isolate starter and auxiliary batteries and allow them to work independently, avoiding shortening battery life due to internal resistances.
- To ensure proper charging. A battery isolator allows two batteries to be charged at the same time using an alternator or charger, while also preventing them from discharging into each other.
- Require emergency start function: When the starter battery is exhausted, the isolator auxiliary switch connects the starter and auxiliary batteries in parallel to fuel the vehicle
- Battery Protection: By isolating and managing each battery independently, a battery isolator helps protect the batteries from damage caused by electrical interference.
Although a battery isolator is usually the preferred option, some systems may use a basic manual switch or alternative isolation methods. But these approaches require more hands-on control and careful monitoring.
How to choose the right battery isolator?
Choosing the right battery isolator requires careful consideration of your needs, battery types, and performance:
Battery Compatibility:
Lead-acid batteries: Use standard relay-based isolators with no voltage drop.
Lithium batteries: Use dedicated isolators or DC-DC chargers to avoid charging damage.
Current Rating & Thermal Design:
≤100A: Standard relay isolators work well for basic RV appliances.
>100A high-load: Use copper-heatsink designs with smart temperature control (for marine propulsion or industrial equipment).
Smart Features Priority:
For universal applications: Choose auto voltage-sensing models that connect at ≥13.3V, disconnect at ≤12.8V.
Special applications, like remote monitoring for Bluetooth-enabled units.
Emergency Function:
A manual parallel override is crucial. This activates an auxiliary battery when the main battery drains, especially for off-grid systems
Low Energy and High-Safety Applications. NiMH batteries are more stable in low-power devices and are suitable for electric toothbrushes.
Key Application Scenarios
- Vehicles/RVs: Use a 150A+ relay isolator with voltage sensing.
- Marine/Energy Storage: Choose 300A thermal-optimized models compatible with lithium packs.
- Industrial Backup Power: Use certified isolators with ≥5000VRMS isolation voltage.
How to install a battery isolator
Universal Installation Steps
- Primary Power Positive Connection
Run ≥25mm² high-temp copper cable from primary power source (vehicle battery/main battery bank) to isolator’s “BAT1” or “Primary” port.
Mandatory Fuse: Install a 150A-300A fuse (lead-acid) / 125% load current fuse (lithium) ≤30cm from the power source.
- Secondary Battery Wiring
Connect isolator’s “BAT2” or “Aux” port → secondary battery positive (same cable gauge).
Grounding Principle: Secondary battery negative → nearest metal frame/ground rod (vehicle chassis or grounding spike for stationary systems)
- Control System Activation
Vehicular: Wire isolator control line to ACC ignition signal (e.g., cigarette lighter fuse slot).
Stationary: Connect to manual switch OR auto-sensing module (engage ≥13.3V / disconnect ≤12.8V).
Always ground the isolator metal casing.
- Emergency Override (Optional)
Extend wires from isolator’s “Normally Open (NO)” terminals → momentary switch.
Press to force parallel connection during primary power failure.
FAQ about Battery isolator
Difference between battery isolator and voltage-sensitive relay (VSR)
A battery isolator controls current flow to protect batteries in dual systems. A VSR is a type of isolator. It connects and disconnects automatically based on voltage levels. For example, it connects at 13.3V or higher and disconnects at 12.8V or lower.
What is the Best battery isolator for an RV?
For RVs, a high-current relay-based isolator (150A+) with automatic voltage sensing is best. It protects the starter battery and simplifies circuit design.
Battery Isolator vs. Battery Splitter
A battery isolator stops simultaneous discharge. It keeps batteries separate for protection. A battery splitter connects batteries in parallel but lacks these safeguards.
Should the battery isolator be on positive or negative?
Battery isolators are installed at the positive terminal for safer and more convenient use. The device does not carry high-voltage electricity after disconnecting the positive terminal, avoiding the risk of electric shock.
Can a Battery Isolator Prevent Theft?
The battery isolator itself does not have an anti-theft function, but it can assist in anti-theft. Firstly, cut-off power isolators reduce the value of theft. Without matching devices, the battery is hard to resell. Secondly, the isolator’s complex structure delays the theft process. Thirdly, the isolator is connected to an anti-theft device to form an anti-theft system, such as an alarm and GPS positioning.